Rejs 30 941 504
Ogromna panorama kulturowa
| Region rejsu : Północna Europa |
| Firma : Oceania Cruises |
| Statek : Sirena |
| Data rozpoczęcia : pon. 11 sie 2025 |
| Data zakończenia : sob. 04 paź 2025 |
| Liczba nocy : 54 nocy |
Harmonogram
| Dzień | Data | Port | Wypłynięcie | Odpłynięcie |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.08 pon. | Reykjavik / Islandia | 06:00 | 18:00 |
| 2 | 12.08 wt. | Isafjordur / Islandia | 08:00 | 16:00 |
| 3 | 13.08 śr. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 4 | 14.08 czw. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 5 | 15.08 pt. | Nuuk / Greenland | 10:00 | 19:00 |
| 6 | 16.08 sob. | Paamiut / Greenland | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 7 | 17.08 niedz. | Kakortok / Greenland | 08:00 | 20:00 |
| 8 | 18.08 pon. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 9 | 19.08 wt. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 10 | 20.08 śr. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 11 | 21.08 czw. | Torshavn / Faroe Islands | 07:00 | 17:00 |
| 12 | 22.08 pt. | Scrubster / Scotland | 09:00 | 18:00 |
| 13 | 23.08 sob. | Aberdeen / Wielka Brytania | 07:00 | 18:00 |
| 14 | 24.08 niedz. | Edynburg / Wielka Brytania | 03:30 | |
| 15 | 25.08 pon. | Edynburg / Wielka Brytania | ||
| 16 | 26.08 wt. | Edynburg / Wielka Brytania | 20:45 | |
| 17 | 27.08 śr. | Kirkwall / Wielka Brytania | 13:00 | 21:00 |
| 18 | 28.08 czw. | Lerwick / Wielka Brytania | 06:00 | 15:00 |
| 19 | 29.08 pt. | Olesunn / Norway | 09:00 | 19:00 |
| 20 | 30.08 sob. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 21 | 31.08 niedz. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 22 | 1.09 pon. | Longyr / Svalbard i Jan Mayen | 07:00 | 21:00 |
| 23 | 2.09 wt. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 24 | 3.09 śr. | Honninsvog / Norway | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 25 | 4.09 czw. | Alta / Norway | 07:00 | 16:00 |
| 26 | 5.09 pt. | Harstad / Norway | 09:00 | 16:00 |
| 27 | 6.09 sob. | Bodo / Norway | 07:00 | 15:00 |
| 28 | 7.09 niedz. | Trondheim / Norway | 11:00 | 19:00 |
| 29 | 8.09 pon. | Måløy | 09:00 | 17:00 |
| 30 | 9.09 wt. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 31 | 10.09 śr. | Używany | 10:00 | 20:00 |
| 32 | 11.09 czw. | IJmuiden | 07:00 | |
| 33 | 12.09 pt. | IJmuiden | 19:00 | |
| 34 | 13.09 sob. | Londyn / Wielka Brytania | 08:00 | 19:00 |
| 35 | 14.09 niedz. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 36 | 15.09 pon. | Belfast / Wielka Brytania | 13:00 | 22:00 |
| 37 | 16.09 wt. | Douglas / Maine Island | 07:00 | 20:00 |
| 38 | 17.09 śr. | Dublin / Irlandia | 06:00 | 17:00 |
| 39 | 18.09 czw. | Plymouth / Wielka Brytania | 12:00 | 19:00 |
| 40 | 19.09 pt. | Paryż / Francja | 08:45 | 21:00 |
| 41 | 20.09 sob. | Dunkirk / Francja | 11:00 | 21:00 |
| 42 | 21.09 niedz. | Antwerpia / Belgia | 09:00 | |
| 43 | 22.09 pon. | Antwerpia / Belgia | 19:00 | |
| 44 | 23.09 wt. | Używany | 06:00 | 16:00 |
| 45 | 24.09 śr. | Paryż / Francja | 07:00 | 21:00 |
| 46 | 25.09 czw. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 47 | 26.09 pt. | Zatoka (Cork) / Irlandia | 07:00 | 18:00 |
| 48 | 27.09 sob. | Dublin / Irlandia | 07:30 | 17:00 |
| 49 | 28.09 niedz. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 50 | 29.09 pon. | Bordeaux / Francja | 12:00 | |
| 51 | 30.09 wt. | Bordeaux / Francja | 12:15 | |
| 51 | 30.09 wt. | Pauillac / Francja | 15:00 | 19:00 |
| 52 | 1.10 śr. | San Sebastian La Gomera San Sebastian la Gomera / Hiszpania | 09:00 | 19:00 |
| 53 | 2.10 czw. | Gijon / Hiszpania | 08:00 | 18:00 |
| 54 | 3.10 pt. | Dzień na morzu / Morze | ||
| 55 | 4.10 sob. | Lizbona / Portugalia | 06:00 | 18:00 |
-
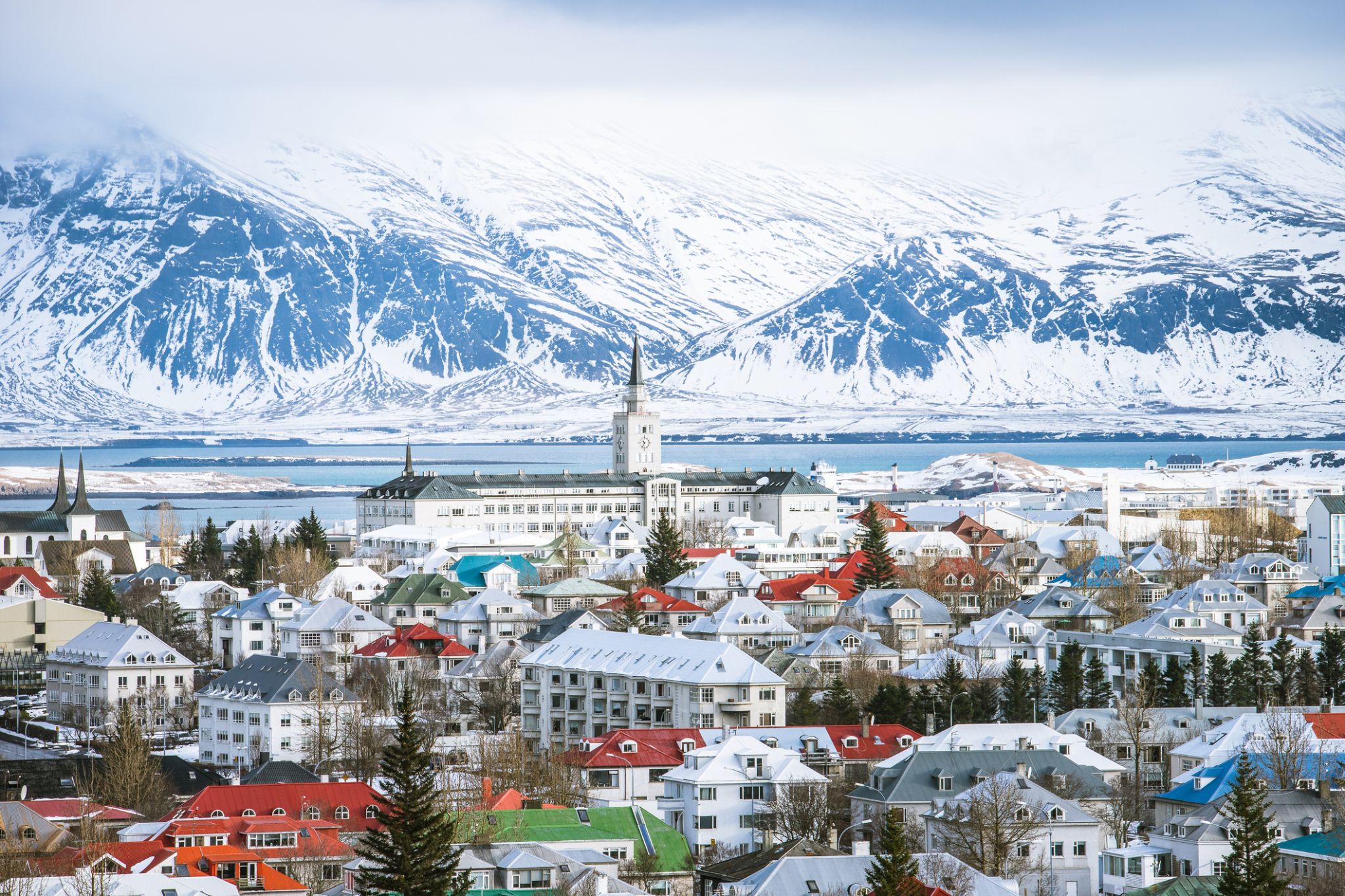 Dzień 1: 06:00-18:00
Dzień 1: 06:00-18:00Reykjavik / Islandia
Reykjavík is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxa Bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a population of around 123,300 (and over 216,940 in the Capital Region), it is the heart of Iceland's cultural, economic and governmental activity, and is a popular tourist destination.
Reykjavík is believed to be the location of the first permanent settlement in Iceland, which, according to Ingólfr Arnarson, was established in AD 874. Until the 19th century, there was no urban development in the city location. The city was founded in 1786 as an official trading town and grew steadily over the following decades, as it transformed into a regional and later national centre of commerce, population, and governmental activities. It is among the cleanest, greenest, and safest cities in the world.
-
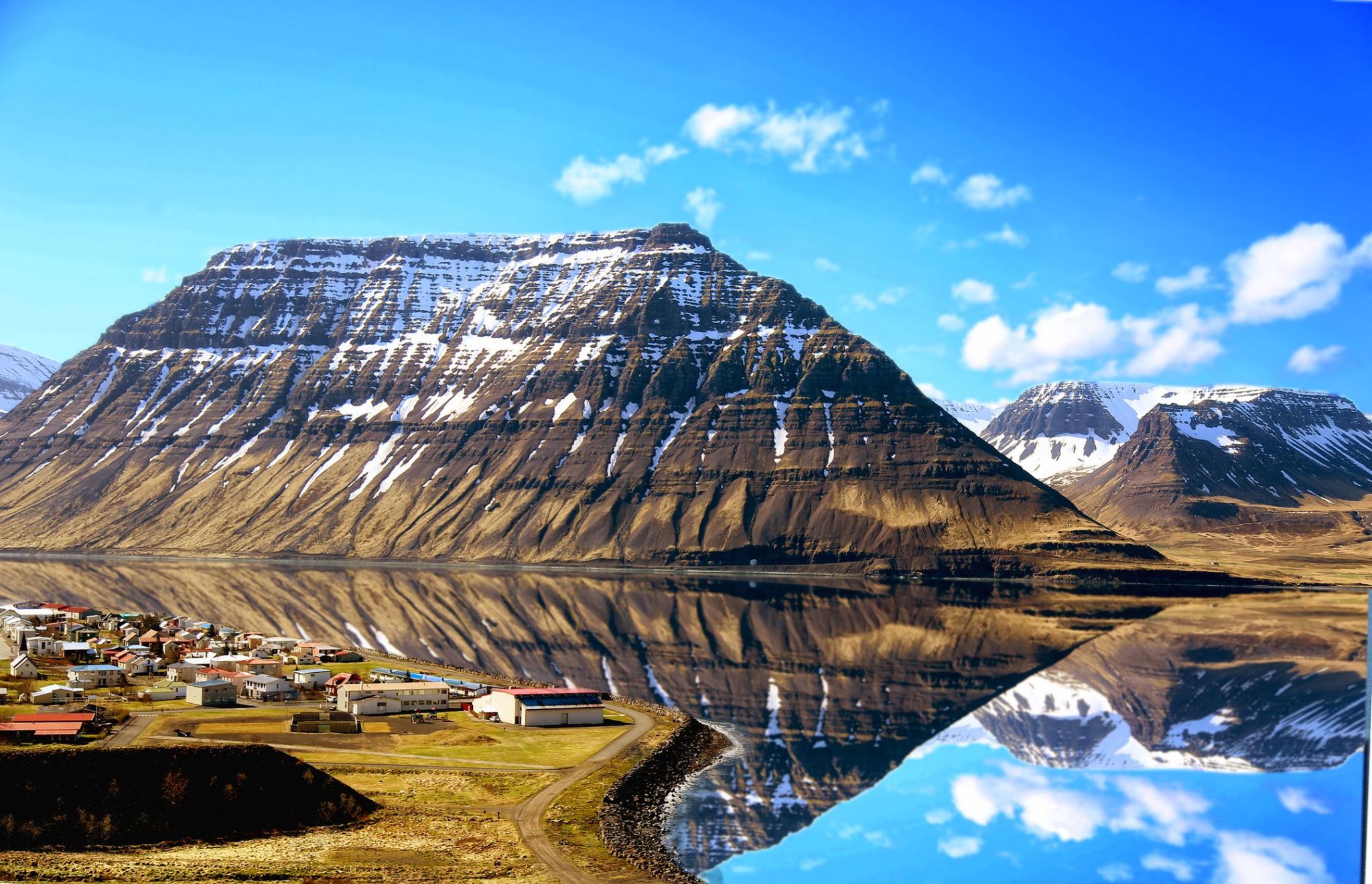 Dzień 2: 08:00-16:00
Dzień 2: 08:00-16:00Isafjordur / Islandia
Isafjörður, meaning ice fjord or fjord of ice, ice in plural genitive) is a town in the northwest of Iceland.
The oldest part of Ísafjörður with the town centre is located on a spit of sand, or eyri, in Skutulsfjörður, a fjord which meets the waters of the larger fjord Ísafjarðardjúp. With a population of about 2,600, Ísafjörður is the largest settlement in the peninsula of Vestfirðir (Westfjords) and the administration centre of the Ísafjarðarbær municipality, which includes – besides Ísafjörður – the nearby villages of Hnífsdalur, Flateyri, Suðureyri, and Þingeyri.
-
 Dzień 3:
Dzień 3:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 4:
Dzień 4:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
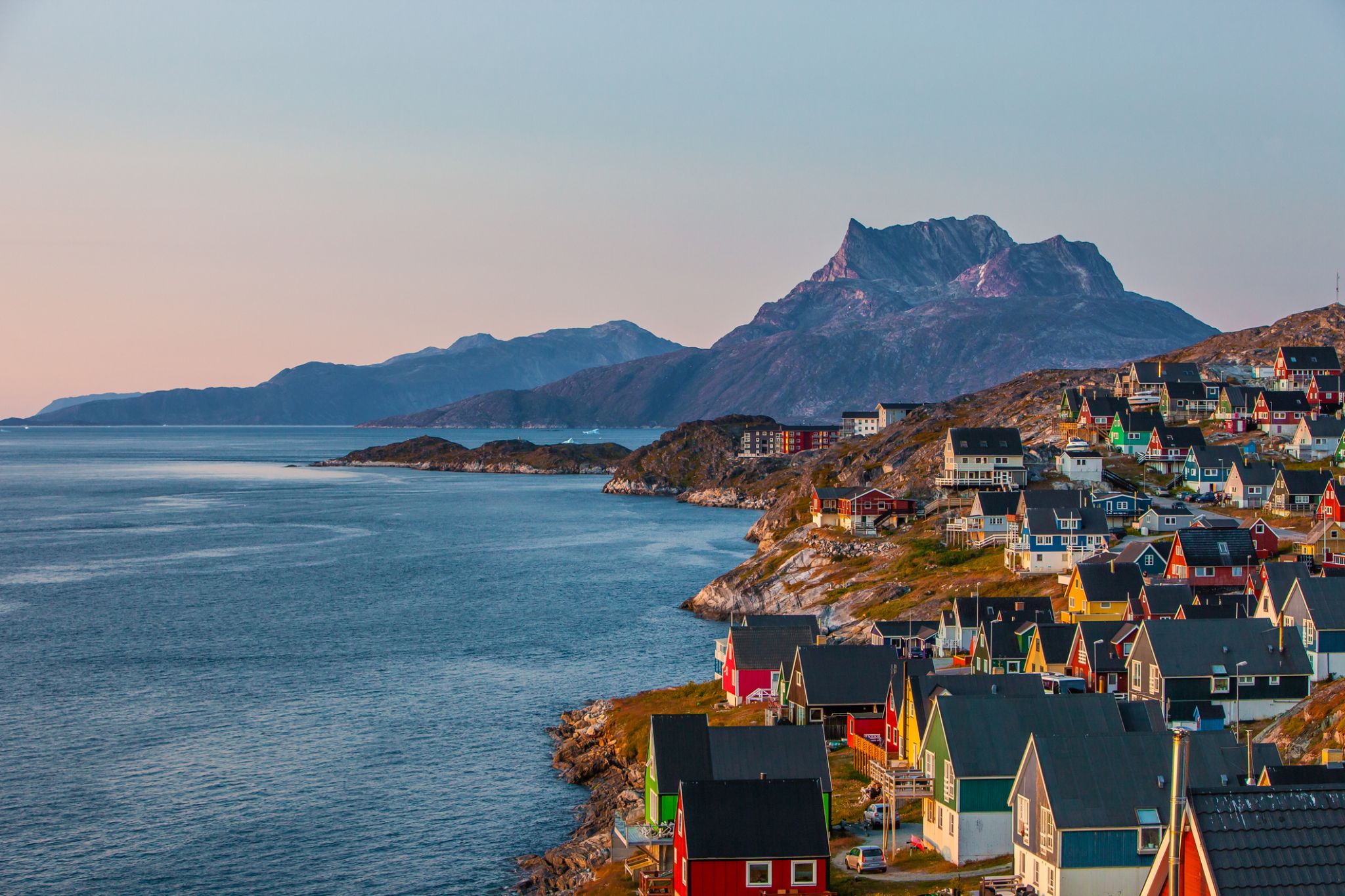 Dzień 5: 10:00-19:00
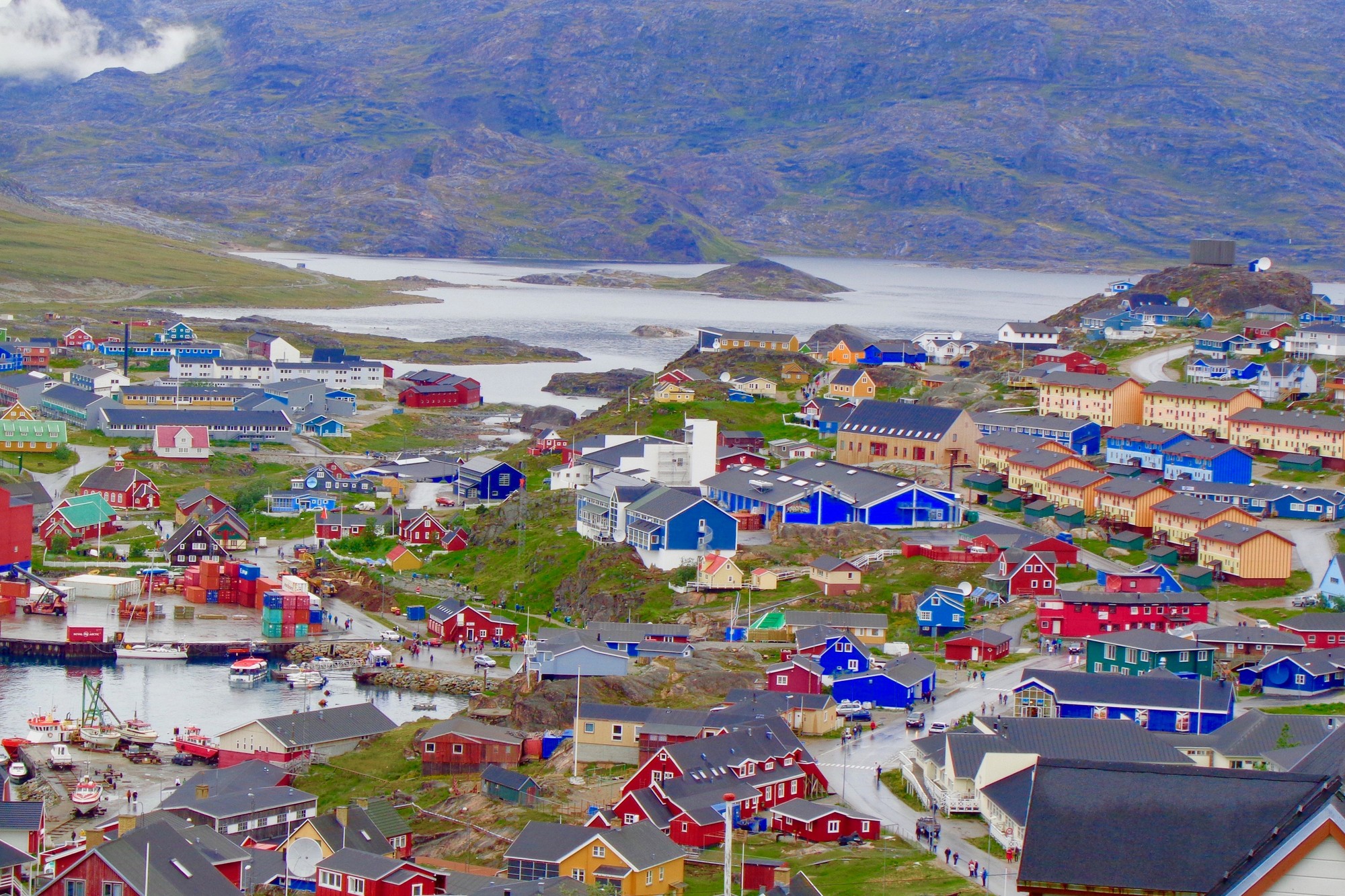
Dzień 5: 10:00-19:00Nuuk / Greenland
-
 Dzień 6: 08:00-18:00
Dzień 6: 08:00-18:00Paamiut / Greenland
-
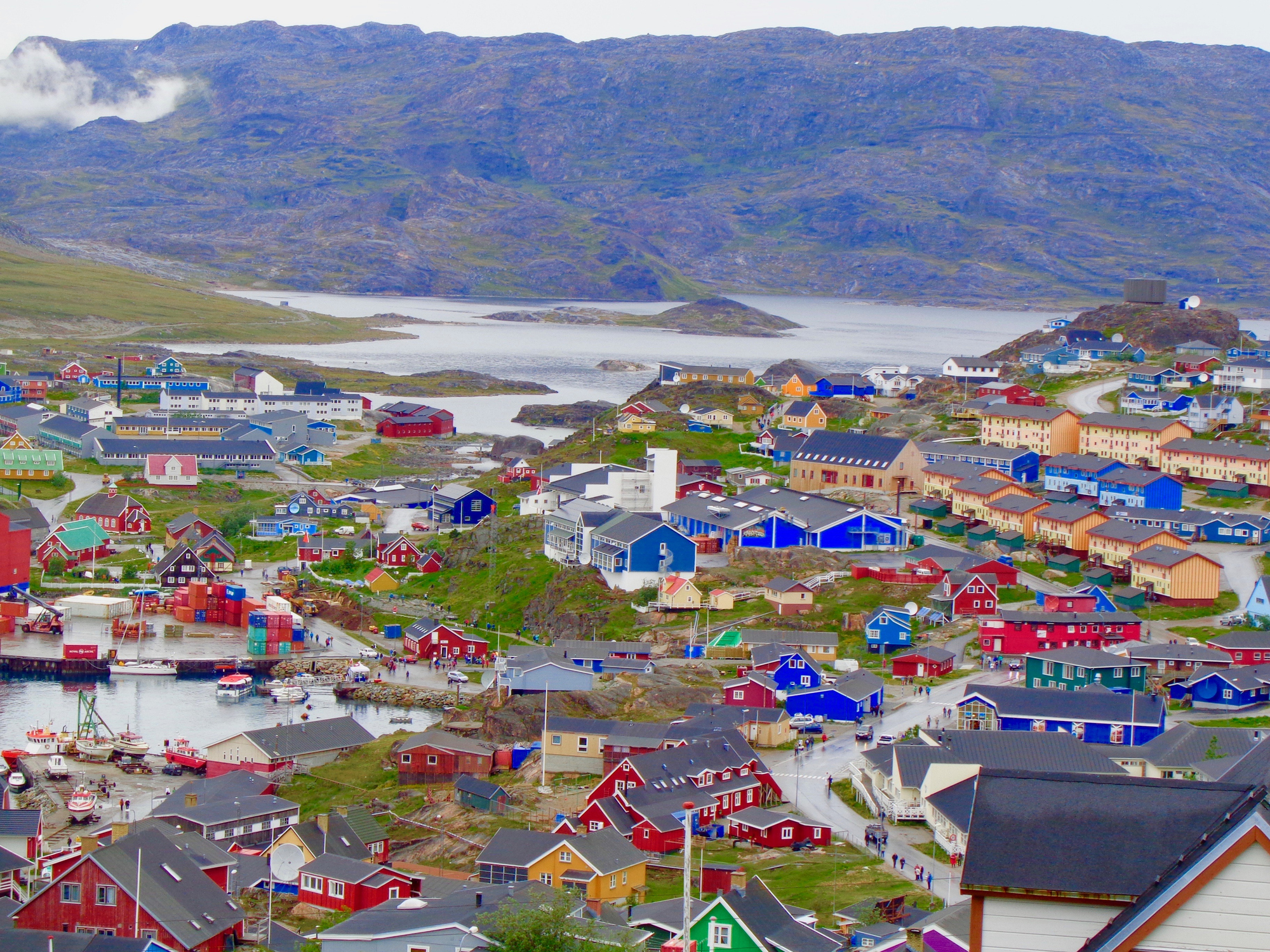 Dzień 7: 08:00-20:00
Dzień 7: 08:00-20:00Kakortok / Greenland
Qaqortoq, formerly Julianehåb, is a town in the Kujalleq municipality in southern Greenland, located near Cape Thorvaldsen. With a population of 3,089 in 2016, it is the most populous town in southern Greenland and the fourth-largest town on the island.
-
 Dzień 8:
Dzień 8:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 9:
Dzień 9:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 10:
Dzień 10:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
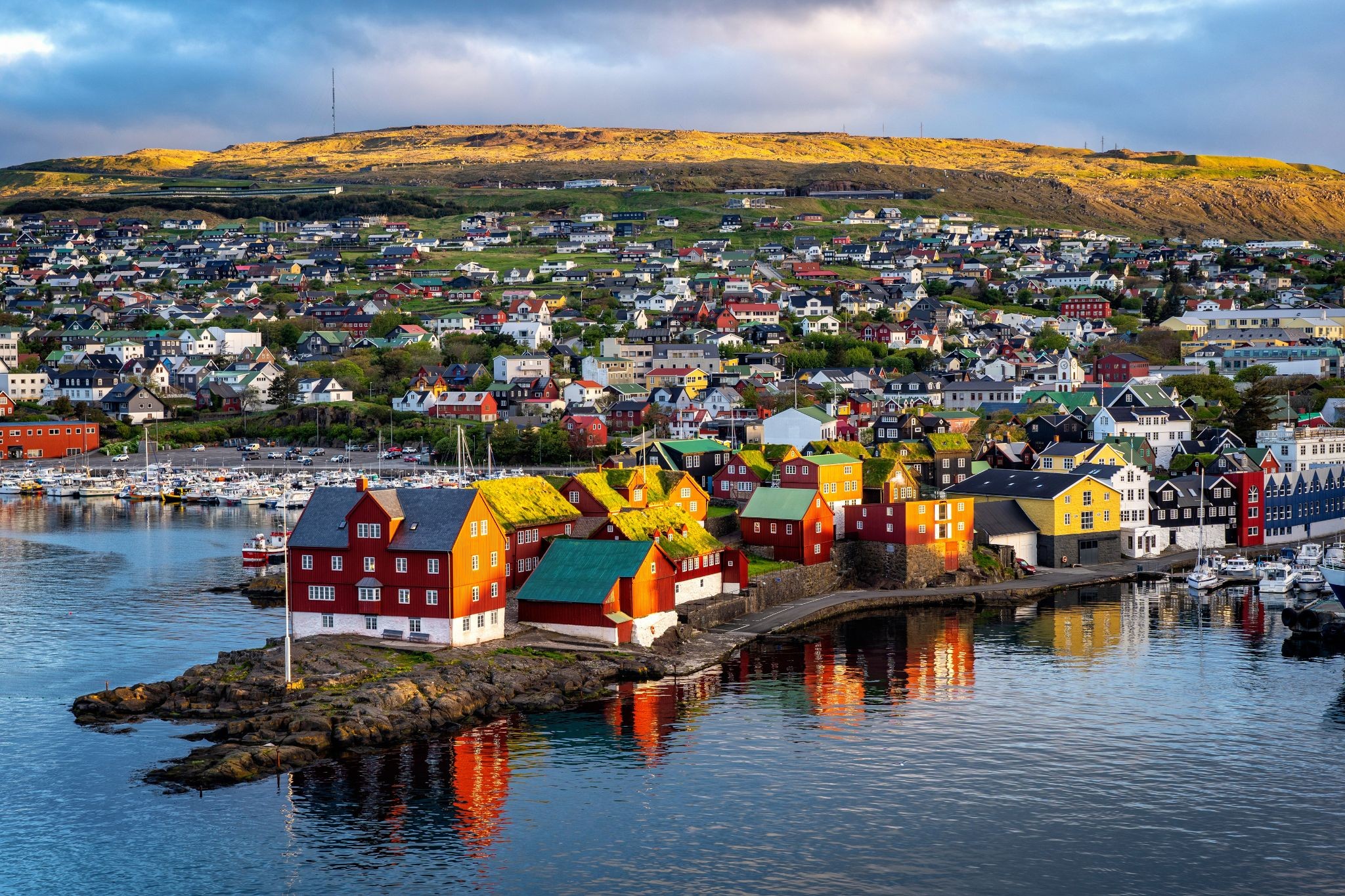
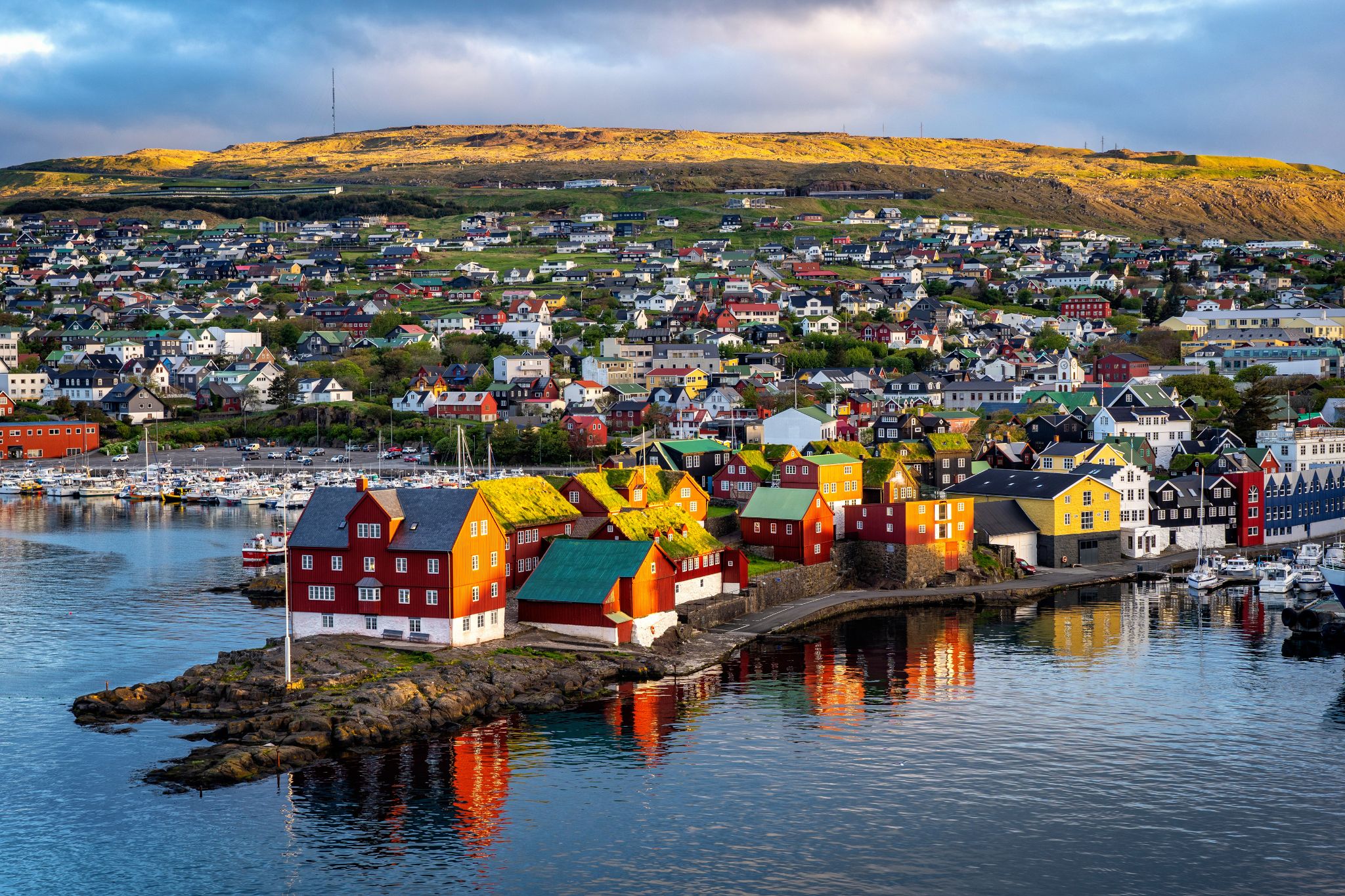 Dzień 11: 07:00-17:00
Dzień 11: 07:00-17:00Torshavn / Faroe Islands
Tórshavn is the capital and largest town of the Faroe Islands. Tórshavn is in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the 347-meter-high (1,138 ft) mountain Húsareyn, and to the southwest, the 350-meter-high (1,150 ft) Kirkjubøreyn. They are separated by the Sandá River. The town proper has a population of 13,089 (2017), and the greater urban area a population of 21,000.
The Norse established their parliament on the Tinganes peninsula in AD 850.[3] Tórshavn thus became the capital of the Faroe Islands and has remained so ever since. All through the Middle Ages the narrow peninsula jutting out into the sea made up the main part of Tórshavn. Early on, Tórshavn became the centre of the islands' trade monopoly, thereby being the only legal place for the islanders to sell and buy goods. In 1856, the trade monopoly was abolished and the islands were left open to free trade.
-
 Dzień 12: 09:00-18:00
Dzień 12: 09:00-18:00Scrubster / Scotland
-
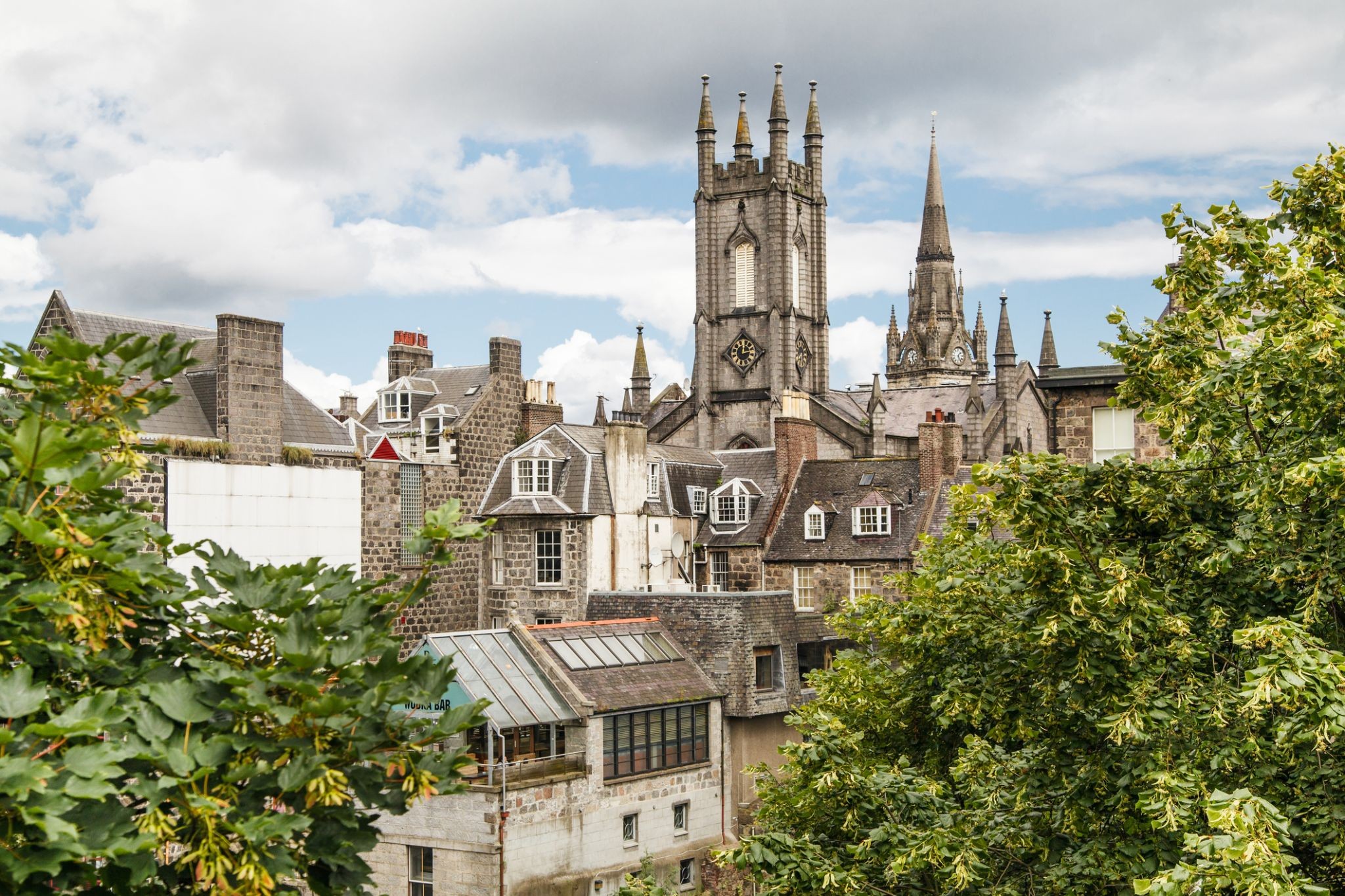
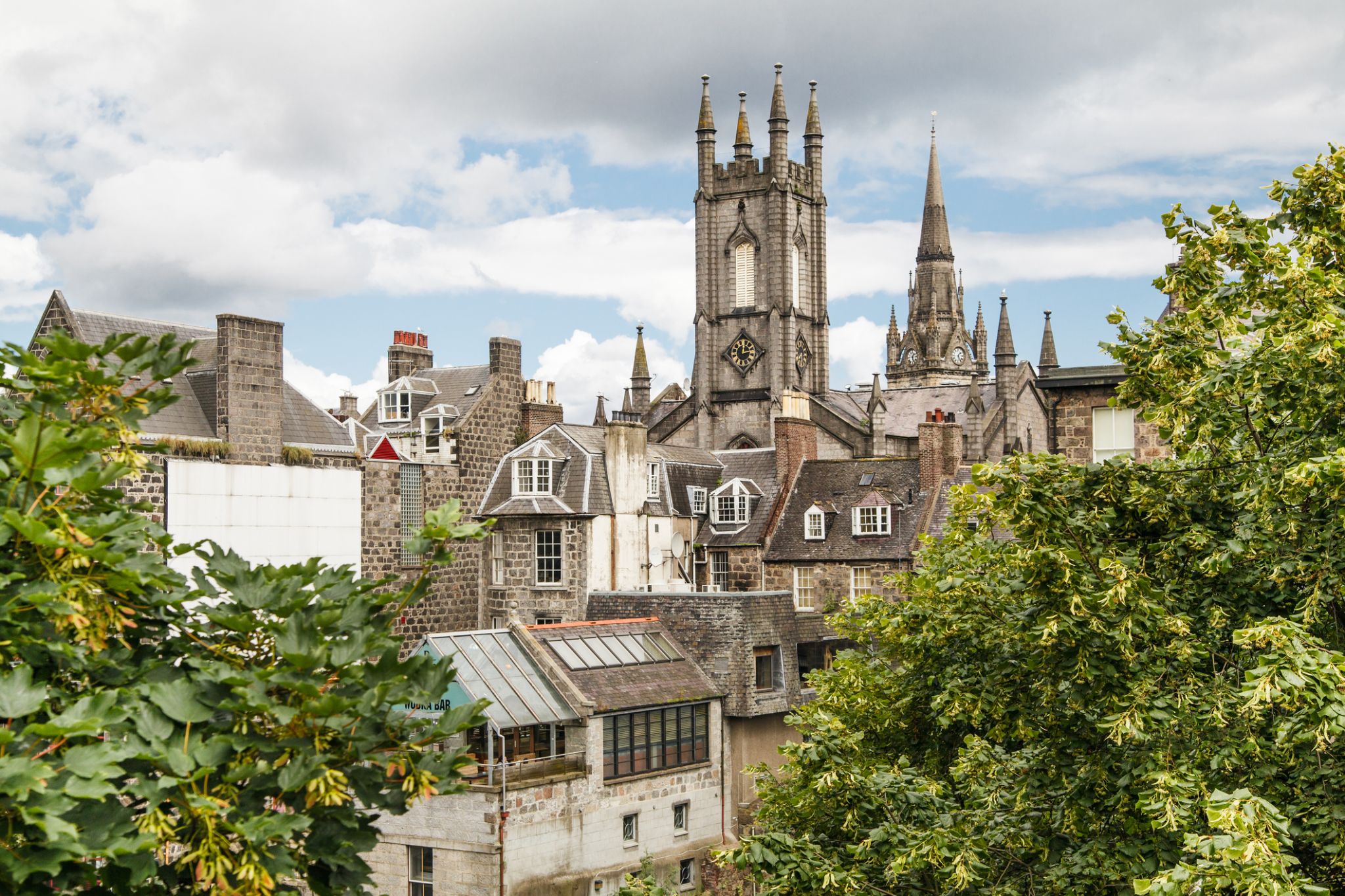 Dzień 13: 07:00-18:00
Dzień 13: 07:00-18:00Aberdeen / Wielka Brytania
-
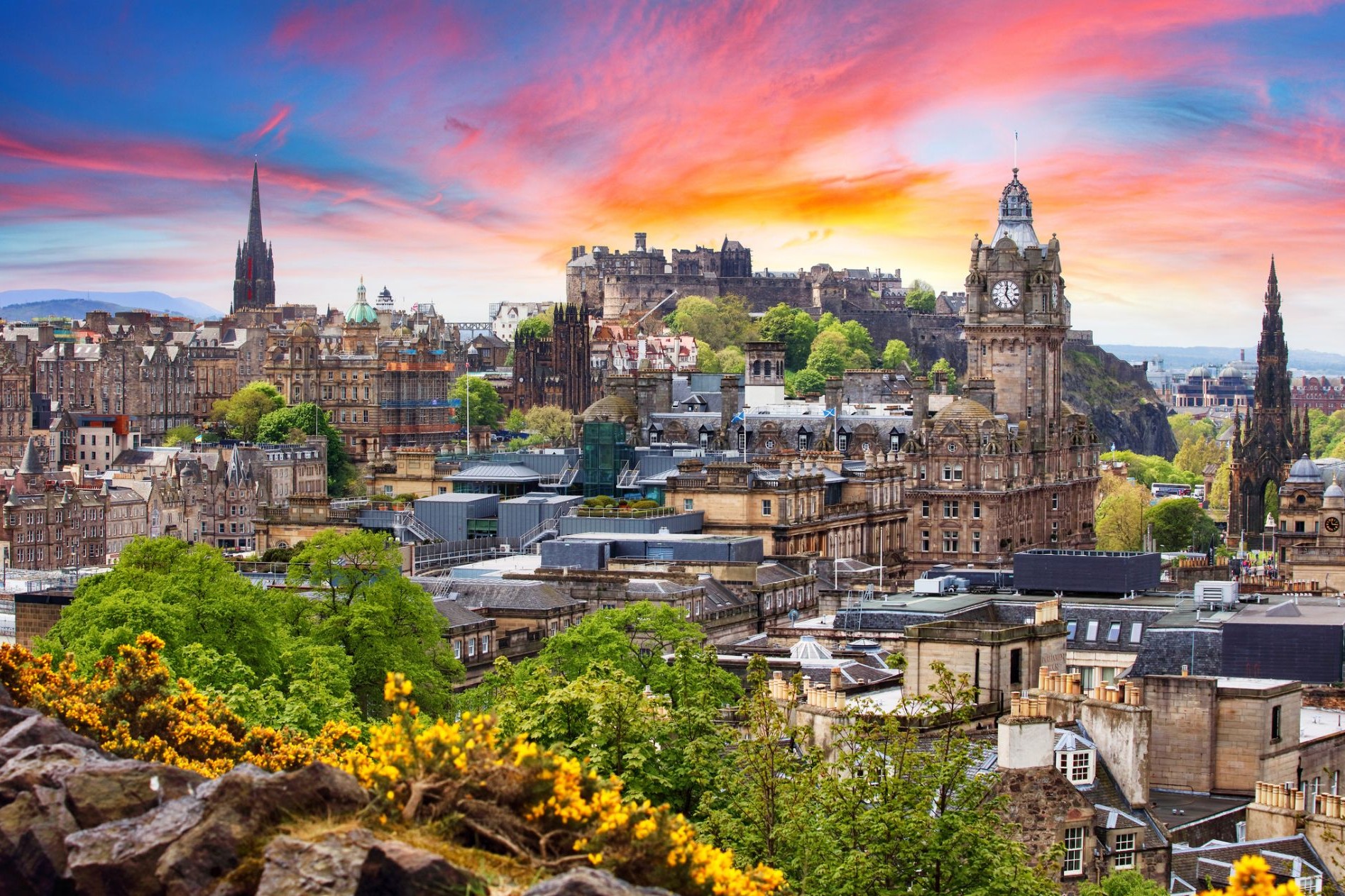
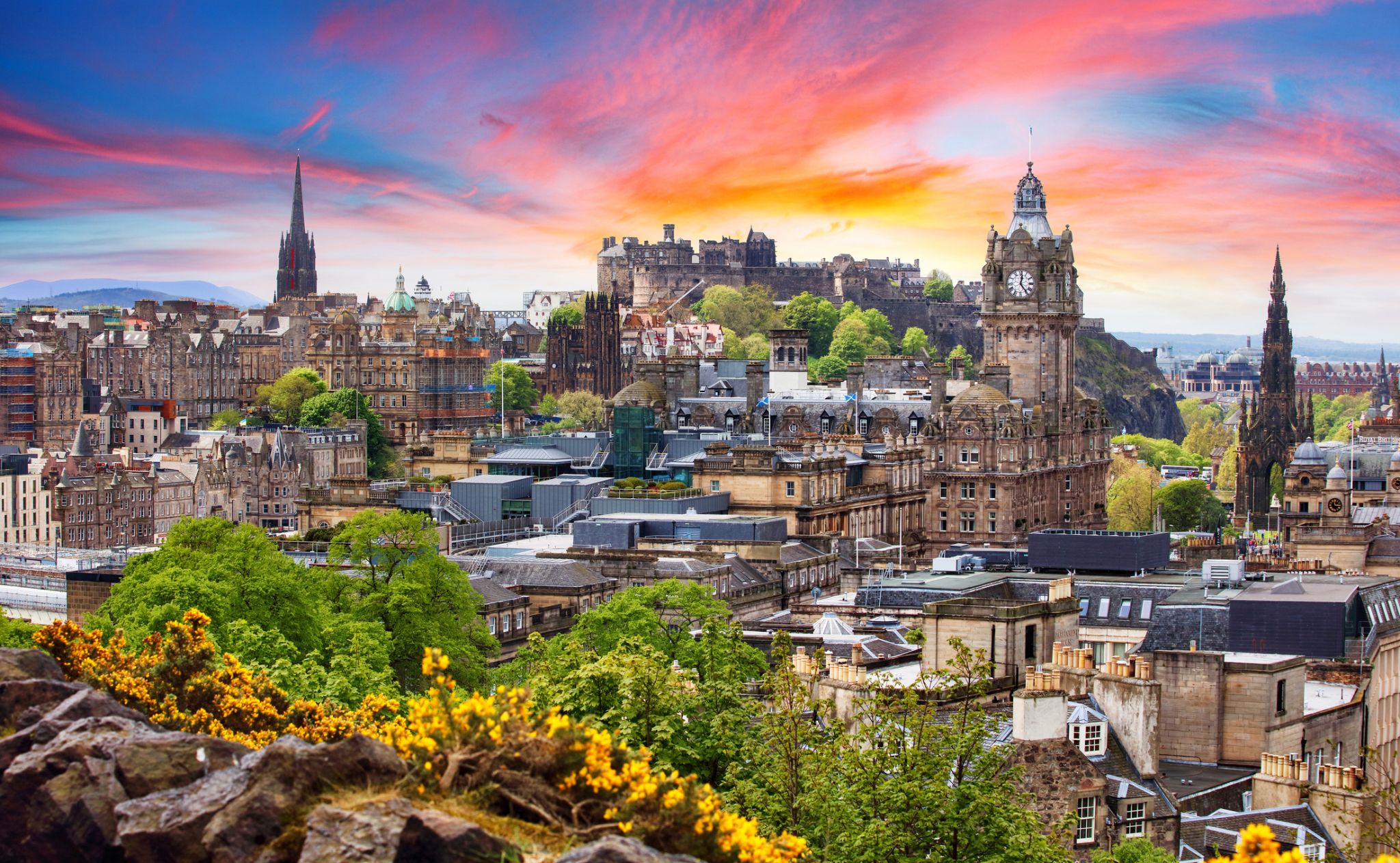 Dzień 14: 03:30
Dzień 14: 03:30Edynburg / Wielka Brytania
-
 Dzień 15:
Dzień 15:Edynburg / Wielka Brytania
-
 Dzień 16: 20:45
Dzień 16: 20:45Edynburg / Wielka Brytania
-
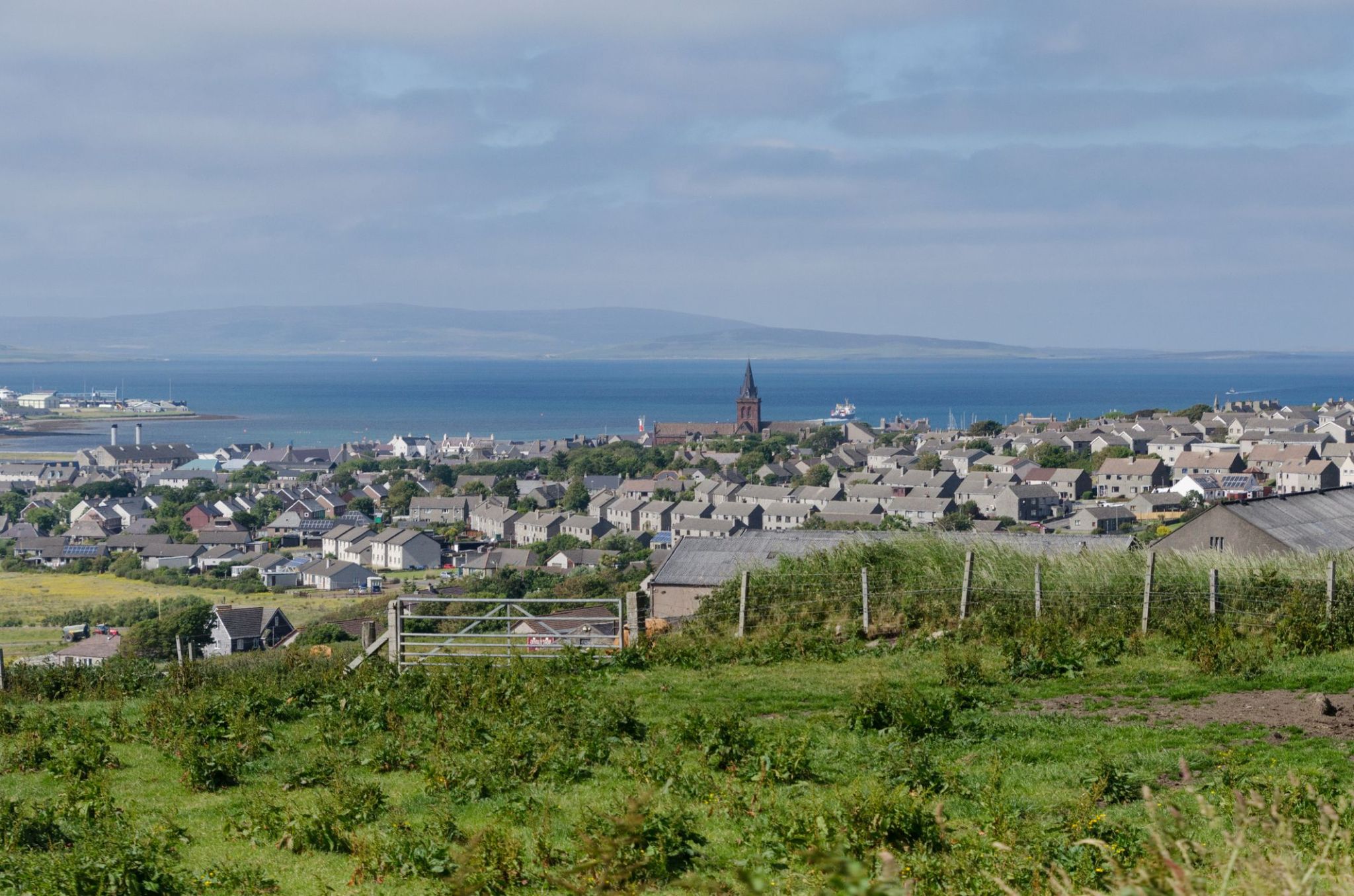 Dzień 17: 13:00-21:00
Dzień 17: 13:00-21:00Kirkwall / Wielka Brytania
-
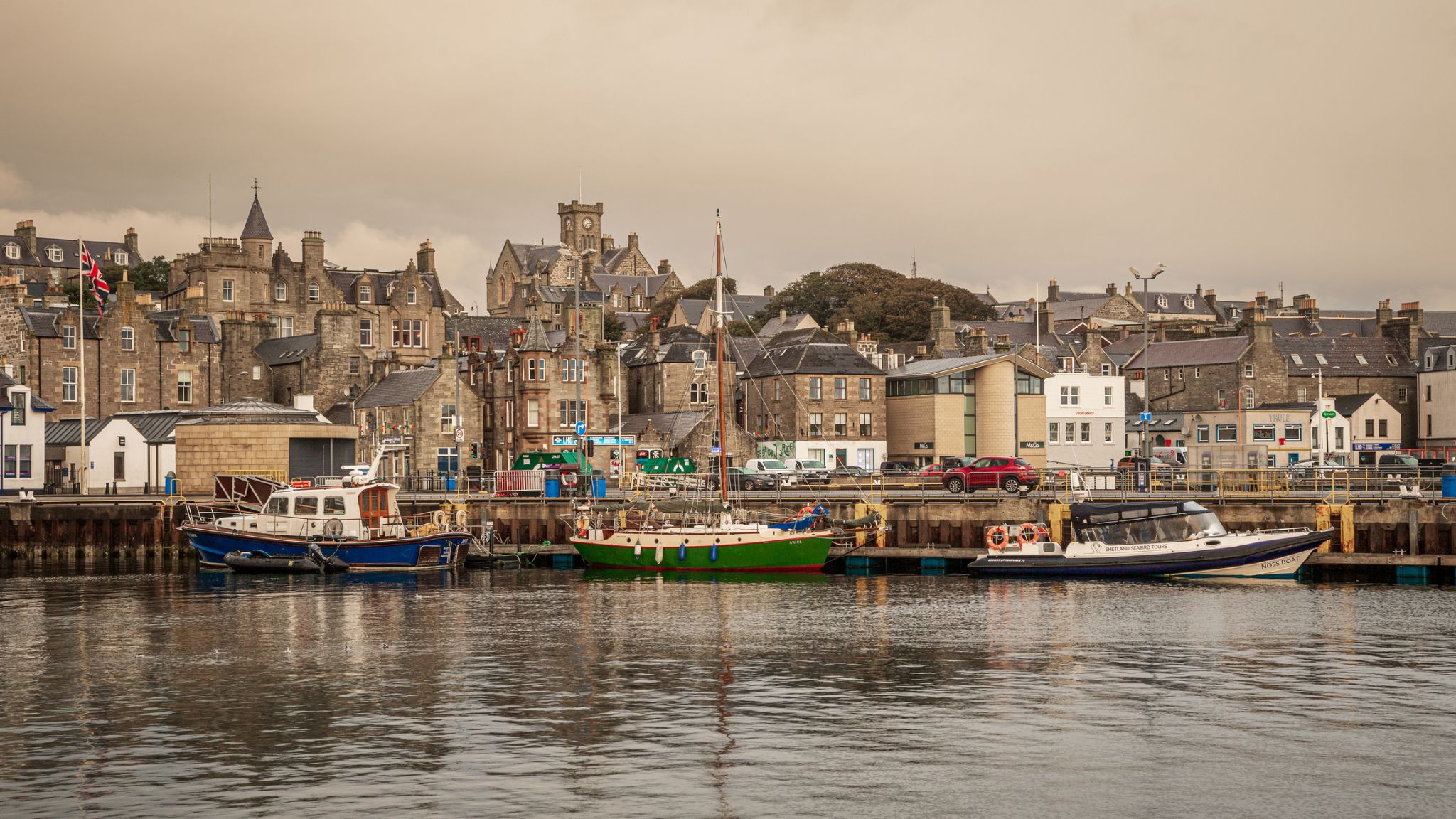 Dzień 18: 06:00-15:00
Dzień 18: 06:00-15:00Lerwick / Wielka Brytania
-
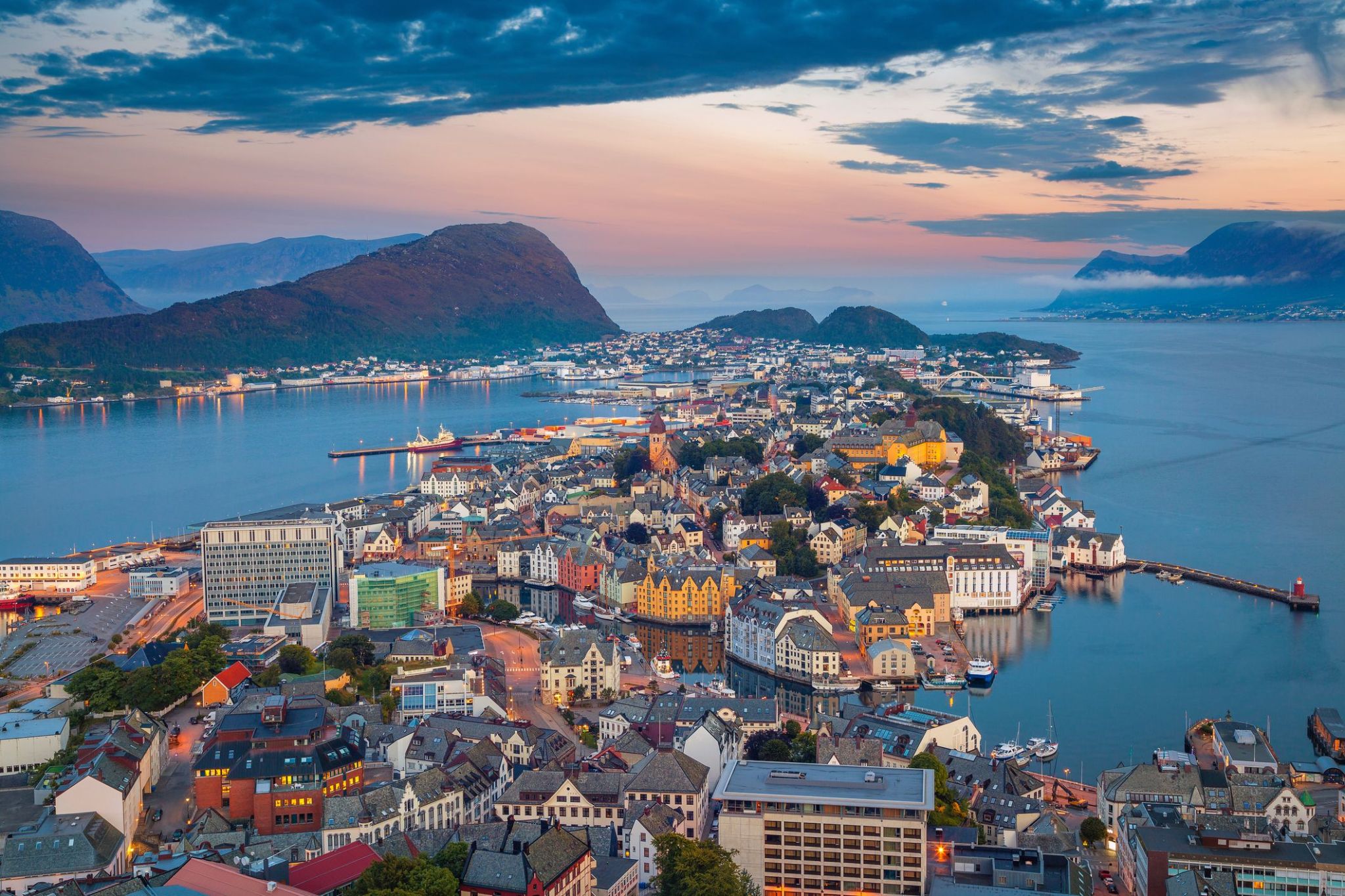 Dzień 19: 09:00-19:00
Dzień 19: 09:00-19:00Olesunn / Norway
-
 Dzień 20:
Dzień 20:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 21:
Dzień 21:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 22: 07:00-21:00
Dzień 22: 07:00-21:00Longyr / Svalbard i Jan Mayen
-
 Dzień 23:
Dzień 23:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
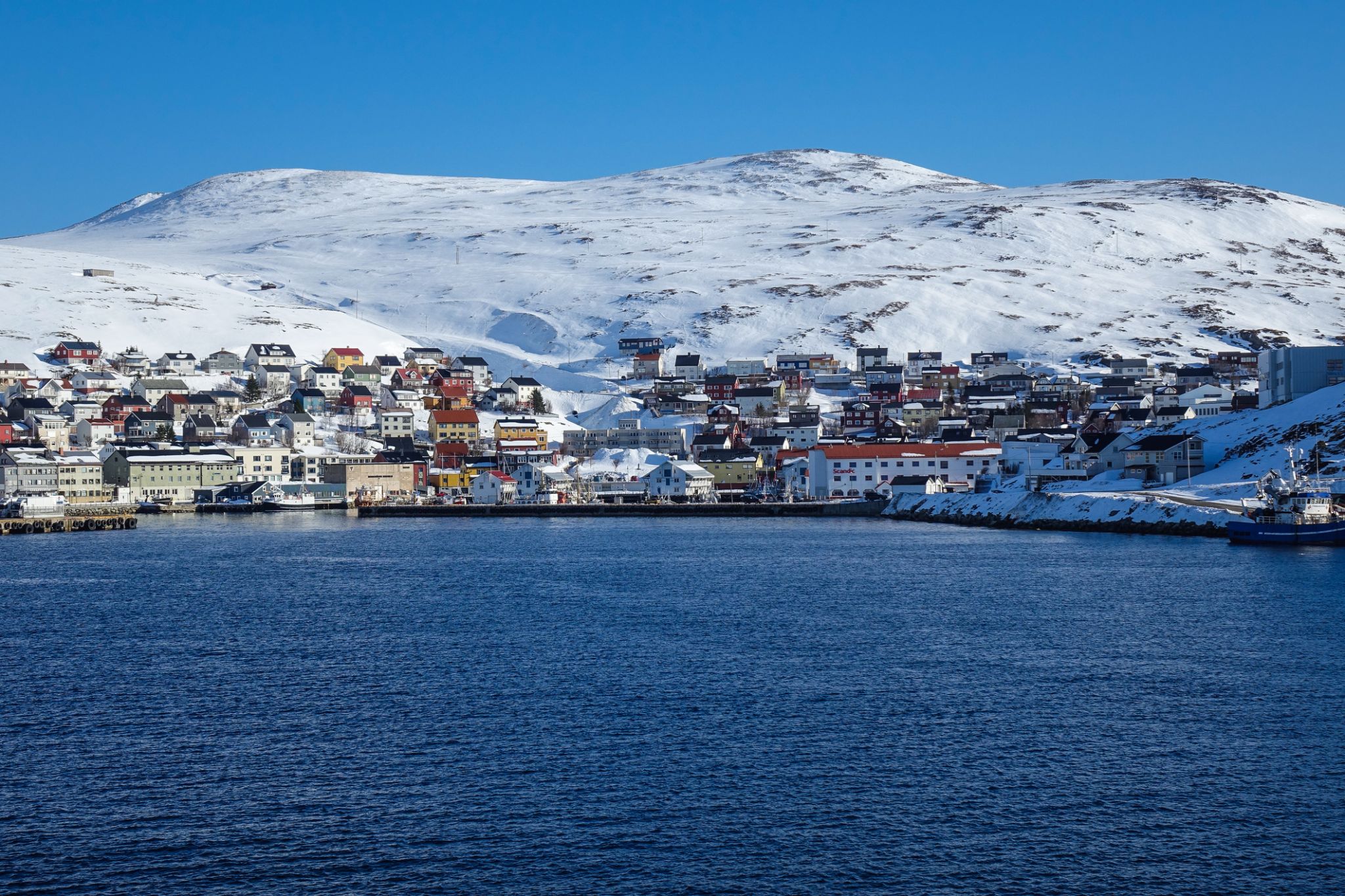 Dzień 24: 08:00-18:00
Dzień 24: 08:00-18:00Honninsvog / Norway
Honningsvåg is the northernmost city in Norway. It is located in Nordkapp Municipality in Finnmark county. Legislation effective in 1997 states that a Norwegian city/town (same word in Norwegian) must have at least 5,000 inhabitants, but Honningsvåg was declared a city in 1996, thus exempt from this legislation, so it is also one of the smallest cities in Norway. The 1.05-square-kilometre (260-acre) town has a population (2017) of 2,484 which gives the town a population density of 2,366 inhabitants per square kilometre (6,130/sq mi).
Honningsvåg is situated at a bay on the southeastern side of the large island of Magerøya, while the famous North Cape and its visitor center is on the northern side of the island. Honningsvåg is a port of call for cruise ships, especially in the summer months. The ice-free ocean (southwestern part of the Barents Sea) provides rich fisheries and tourism is also important to the town. Even at 71°N, many private gardens in Honningsvåg have trees, although rarely more than 3 to 4 metres (9.8 to 13.1 ft) tall.
-
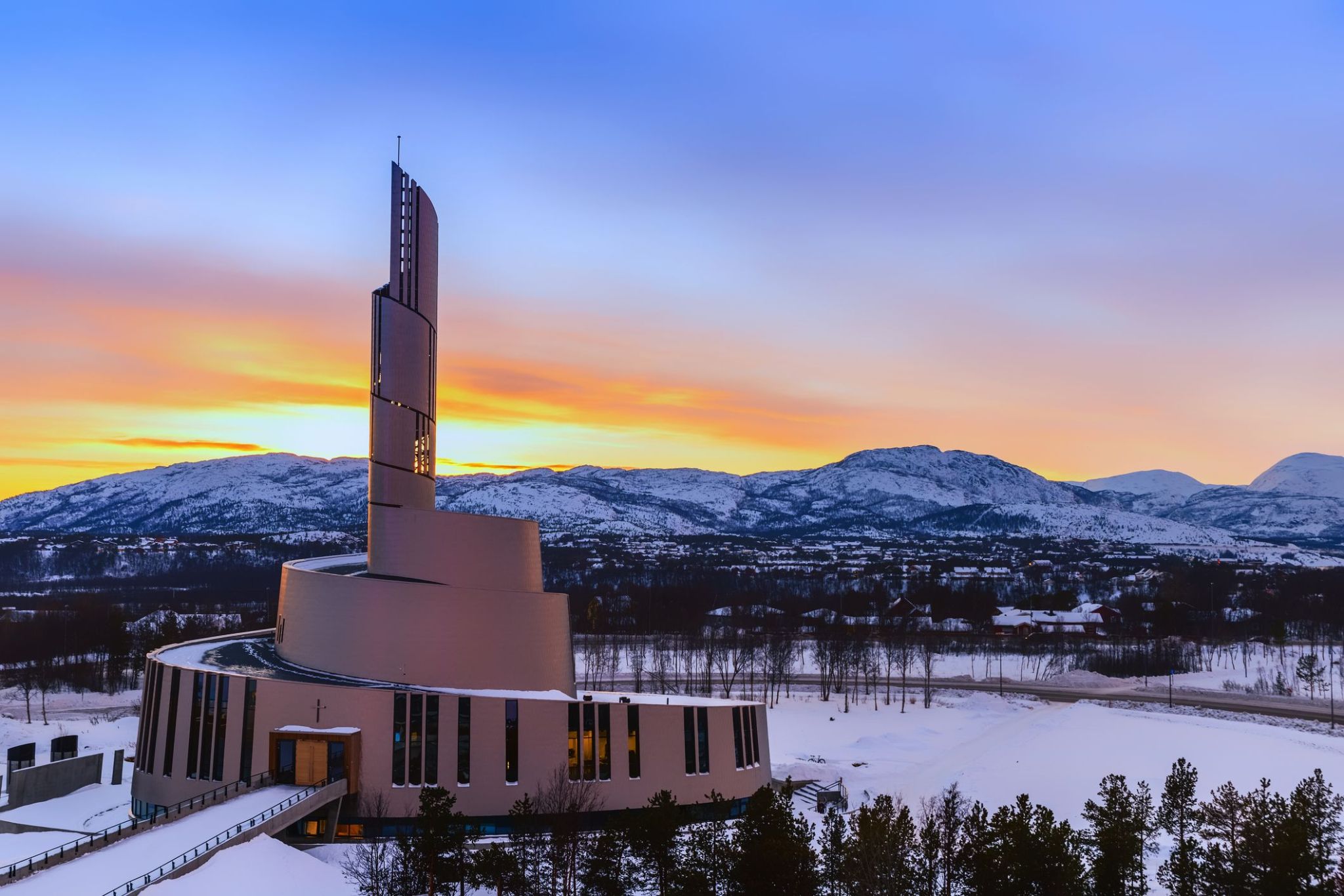 Dzień 25: 07:00-16:00
Dzień 25: 07:00-16:00Alta / Norway
Zanurzona w atmosferze majestatycznej północy, Alta w Norwegii oferuje wyjątkowe połączenie dzikiej przyrody, dziedzictwa kulturowego i arktycznego spokoju. To miasto w regionie Finnmark słynie ze starożytnych rytów naskalnych wpisanych na listę światowego dziedzictwa UNESCO oraz z jednych z najlepszych widoków na zorzę polarną w kraju. Alta to także punkt wyjścia do wypraw na płaskowyż arktyczny i niezapomnianych wycieczek przez lodowe jaskinie i ośnieżone lasy.
Alta to nie tylko miejsce cudów natury, ale także centrum nowoczesnej północy, gdzie tradycje Saamów harmonijnie łączą się z norweską innowacyjnością. Można tu odwiedzić słynny lodowy hotel Sorrisniva, skosztować zupy z ryb arktycznych lub przejechać się psim zaprzęgiem. O każdej porze roku miasto zaprasza podróżnych do ponownego odkrywania północy — z ciepłem, gościnnością i niezapomnianymi przygodami za kołem podbiegunowym.
-
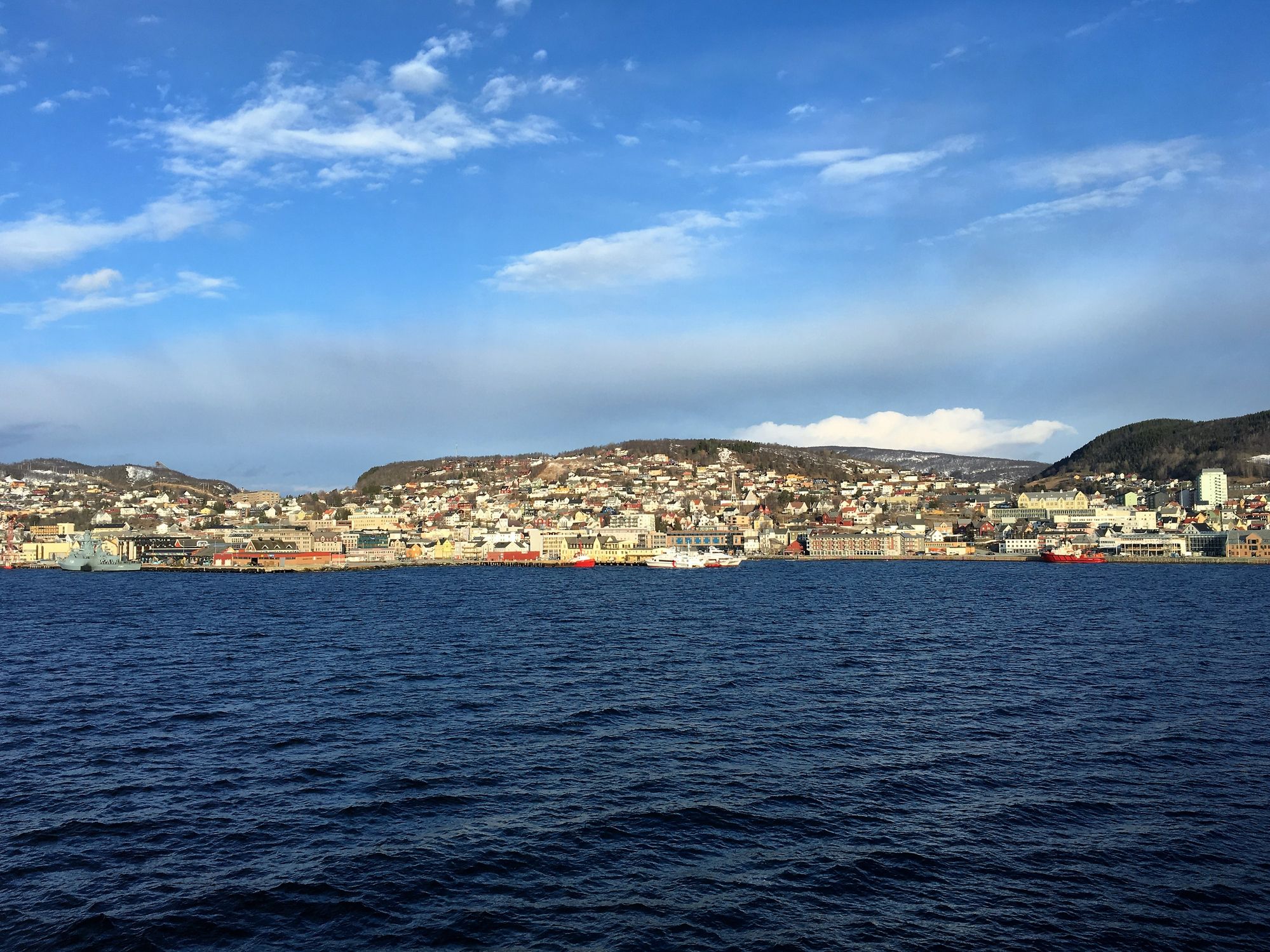 Dzień 26: 09:00-16:00
Dzień 26: 09:00-16:00Harstad / Norway
-
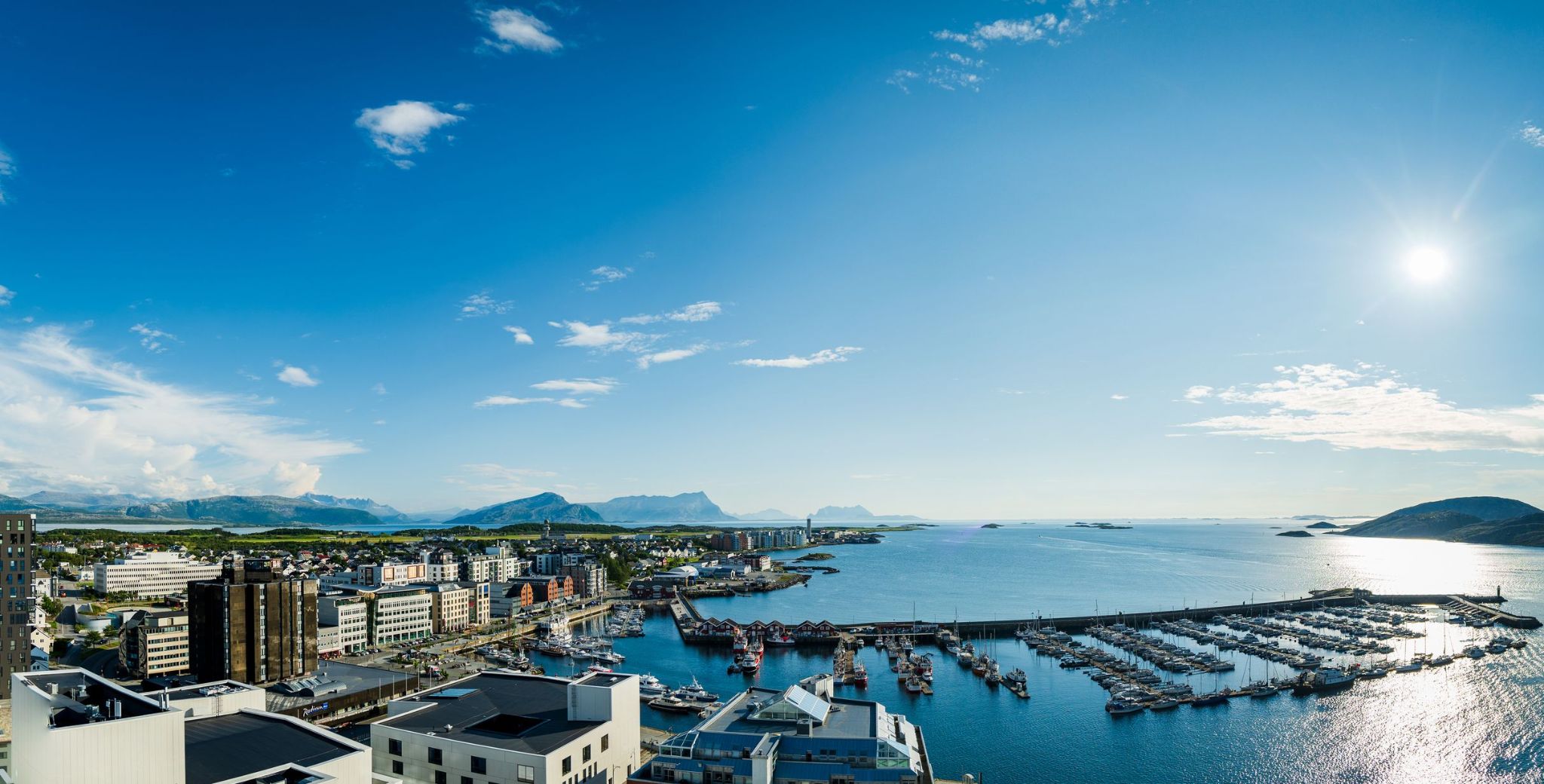 Dzień 27: 07:00-15:00
Dzień 27: 07:00-15:00Bodo / Norway
-
 Dzień 28: 11:00-19:00
Dzień 28: 11:00-19:00Trondheim / Norway
-
 Dzień 29: 09:00-17:00
Dzień 29: 09:00-17:00Måløy
-
 Dzień 30:
Dzień 30:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
 Dzień 31: 10:00-20:00
Dzień 31: 10:00-20:00Używany
-
 Dzień 32: 07:00
Dzień 32: 07:00IJmuiden
-
 Dzień 33: 19:00
Dzień 33: 19:00IJmuiden
-
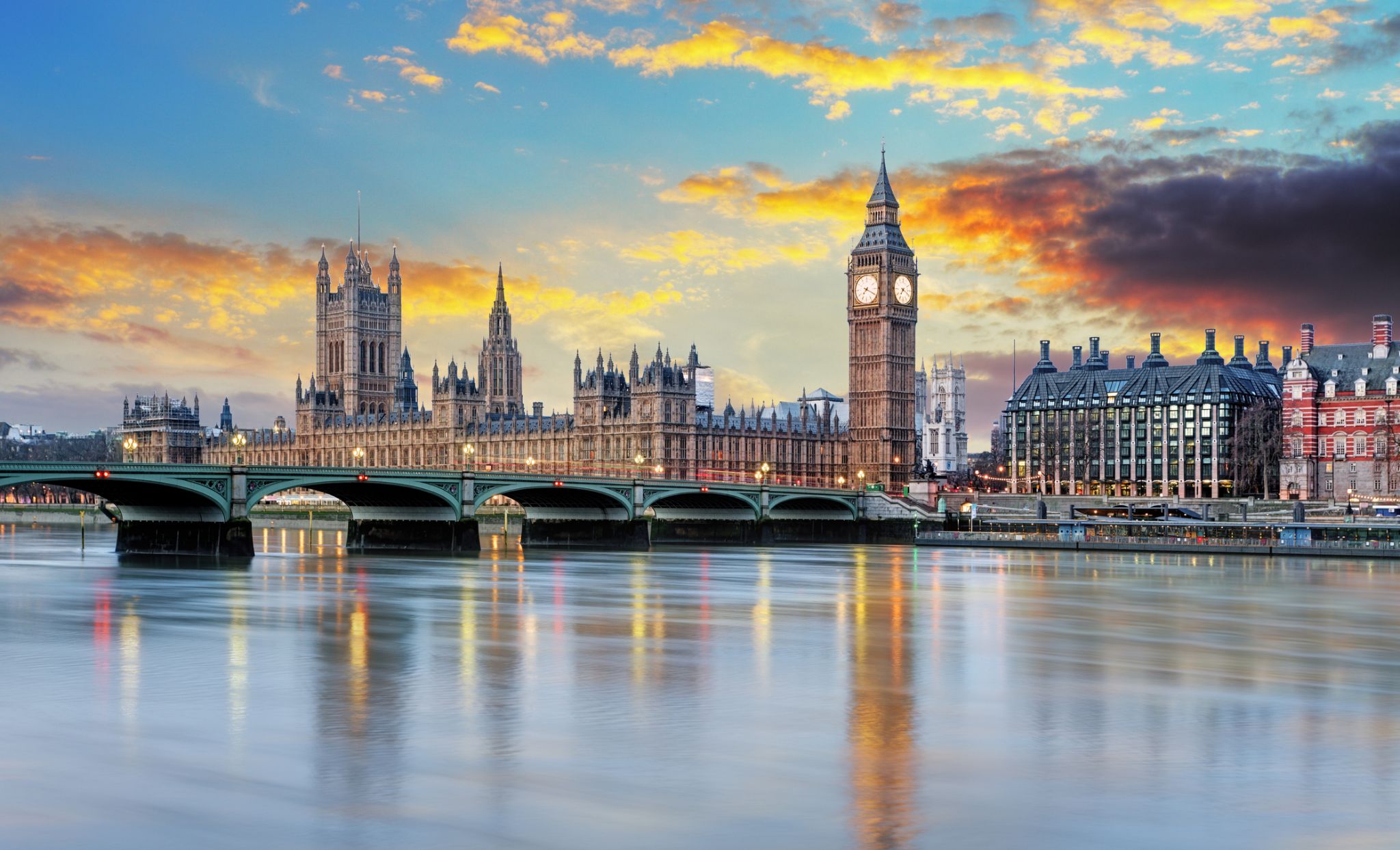 Dzień 34: 08:00-19:00
Dzień 34: 08:00-19:00Londyn / Wielka Brytania
-
 Dzień 35:
Dzień 35:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
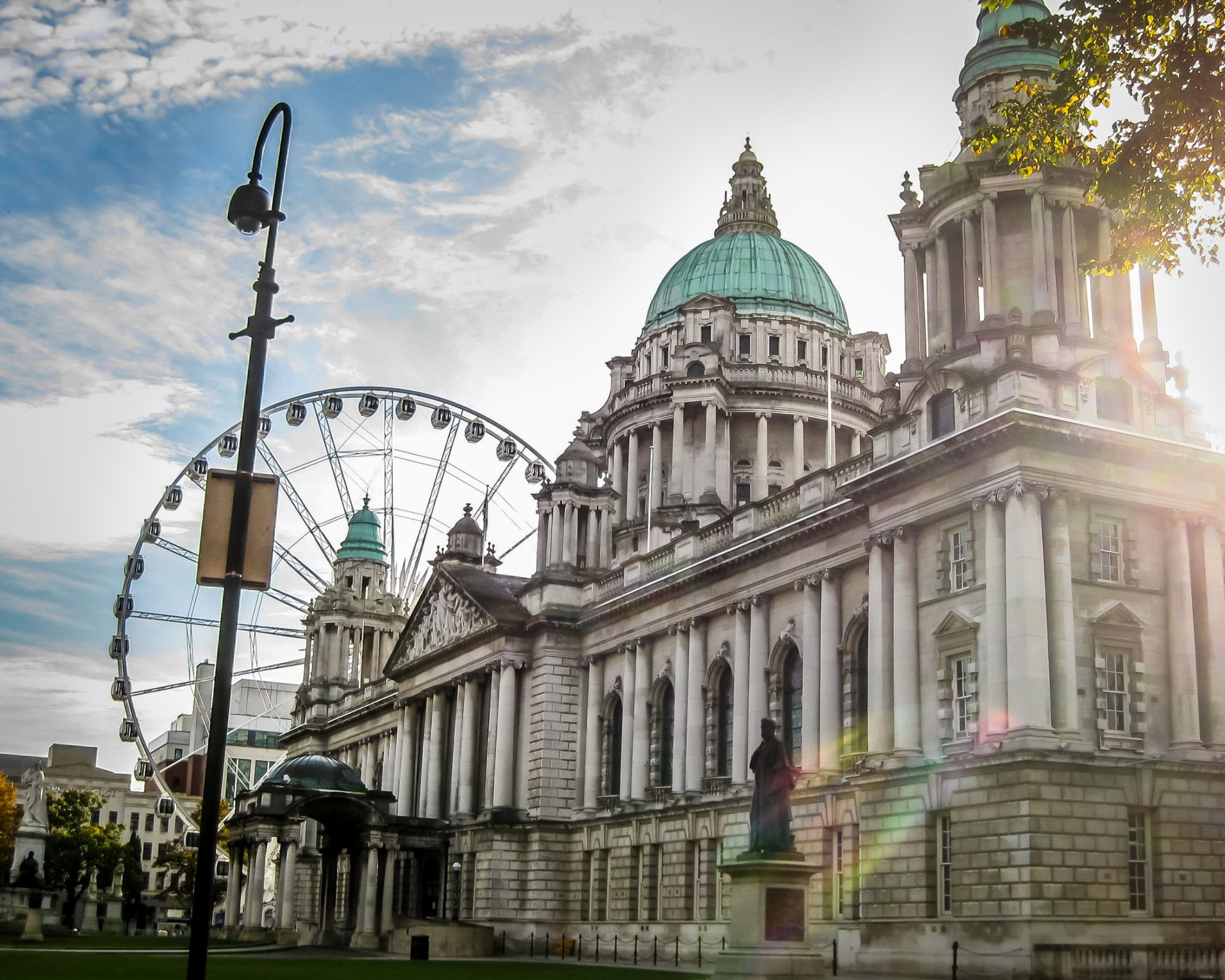 Dzień 36: 13:00-22:00
Dzień 36: 13:00-22:00Belfast / Wielka Brytania
Belfast is a port city in the United Kingdom and the capital city of Northern Ireland, on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast of Ireland. It is the largest city in Northern Ireland and second largest on the island of Ireland. It had a population of 333,871 in 2015.
By the early 1800s Belfast was a major port. It played a key role in the Industrial Revolution, becoming the biggest linen producer in the world, earning it the nickname "Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, where the RMS Titanic was built, was the world's biggest shipyard. It also has a major aerospace and missiles industry. Industrialisation and the inward migration it brought made Belfast Ireland's biggest city and it became the capital of Northern Ireland following the Partition of Ireland in 1922. Its status as a global industrial centre ended in the decades after the Second World War.
Belfast suffered greatly in the Troubles, and in the 1970s and 1980s was one of the world's most dangerous cities. However, the city is now considered to be one of the safest within the United Kingdom. Throughout the 21st century, the city has seen a sustained period of calm, free from the intense political violence of former years and has benefitted from substantial economic and commercial growth. Belfast remains a centre for industry, as well as the arts, higher education, business, and law, and is the economic engine of Northern Ireland. Belfast is still a major port, with commercial and industrial docks dominating the Belfast Lough shoreline, including the Harland and Wolff shipyard. It is served by two airports: George Best Belfast City Airport, and Belfast International Airport 15 miles (24 km) west of the city. It is listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a Gamma global city.
-
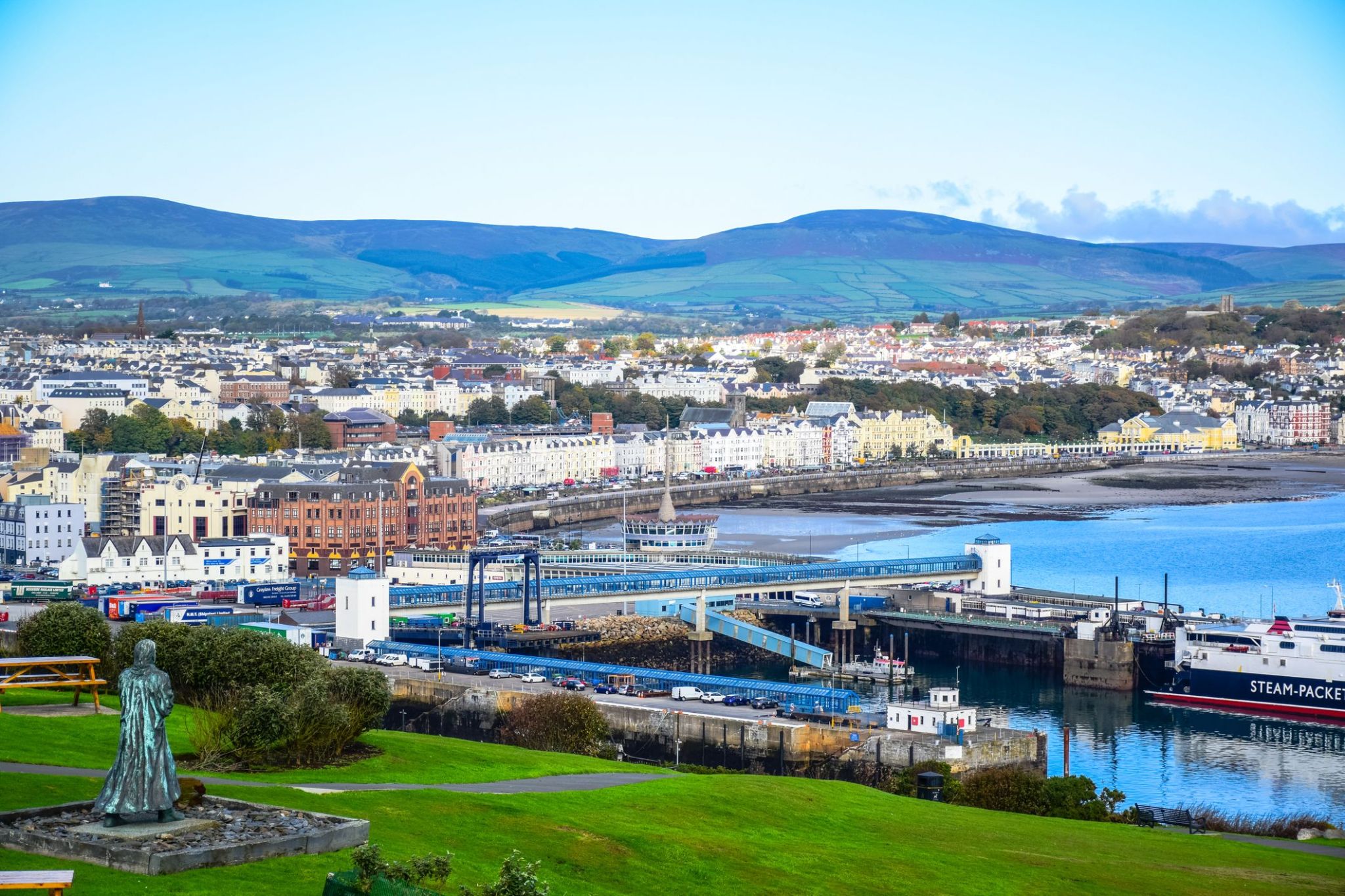 Dzień 37: 07:00-20:00
Dzień 37: 07:00-20:00Douglas / Maine Island
Douglas to stolica i największe miasto Wyspy Man, położone w Morzu Irlandzkim. Miasto, które ma bogatą historię morską, jest znane z malowniczych krajobrazów wybrzeża oraz przytulnej atmosfery. W Douglasie można spacerować po historycznej promenadzie, gdzie znajdują się zabytkowe budynki i nowoczesne kawiarnie, a także odwiedzić lokalne muzeum, które opowiada o morskiej kulturze i tradycjach wyspy. Miasto jest również znane z architektonicznych zabytków, takich jak zamek i historyczne budynki wiktoriańskie, które nadają mu wyjątkowy urok.
Okolice Douglas oferują doskonałe możliwości do aktywnego wypoczynku, w tym wędrówki, spacery wzdłuż wybrzeża i wycieczki rowerowe. Wyspa Man słynie z unikalnej przyrody, a turyści mogą podziwiać widoki na wzgórza, malownicze zatoki i tradycyjne wioski. Ten zakątek Wielkiej Brytanii przyciąga turystów swoją unikalną kulturą, starodawnymi tradycjami oraz pięknymi naturalnymi krajobrazami, co sprawia, że jest to idealne miejsce na relaksujący wypoczynek i ekscytujące podróże.
-
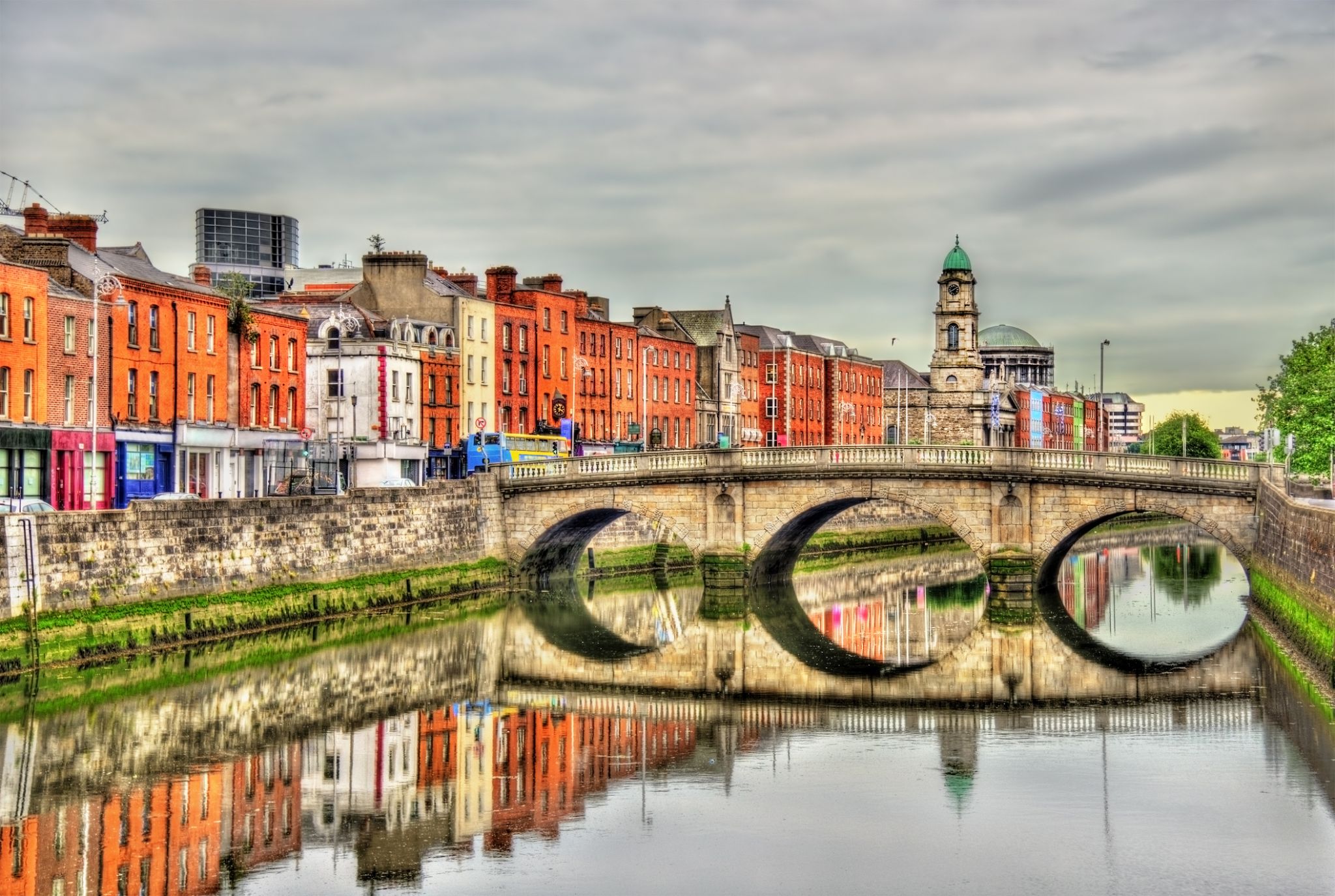 Dzień 38: 06:00-17:00
Dzień 38: 06:00-17:00Dublin / Irlandia
Dublin is the capital of, and largest city in, Ireland. It is on the east coast of Ireland, in the province of Leinster, at the mouth of the River Liffey, and is bordered on the south by the Wicklow mountains. It has an urban area population of 1,173,179, while the population of the Dublin Region (formerly County Dublin), as of 2016, was 1,347,359, and the population of the Greater Dublin area was 1,904,806.
There is archaeological debate regarding precisely where Dublin was established by Celtic-speaking people in the 7th century AD. Later expanded as a Viking settlement, the Kingdom of Dublin, the city became Ireland's principal settlement following the Norman invasion. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest city in the British Empire before the Acts of Union in 1800. Following the partition of Ireland in 1922, Dublin became the capital of the Irish Free State, later renamed Ireland.
Dublin is a historical and contemporary centre for education, the arts, administration and industry. As of 2018 the city was listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a global city, with a ranking of "Alpha -", which places it amongst the top thirty cities in the world.
-
 Dzień 39: 12:00-19:00
Dzień 39: 12:00-19:00Plymouth / Wielka Brytania
-
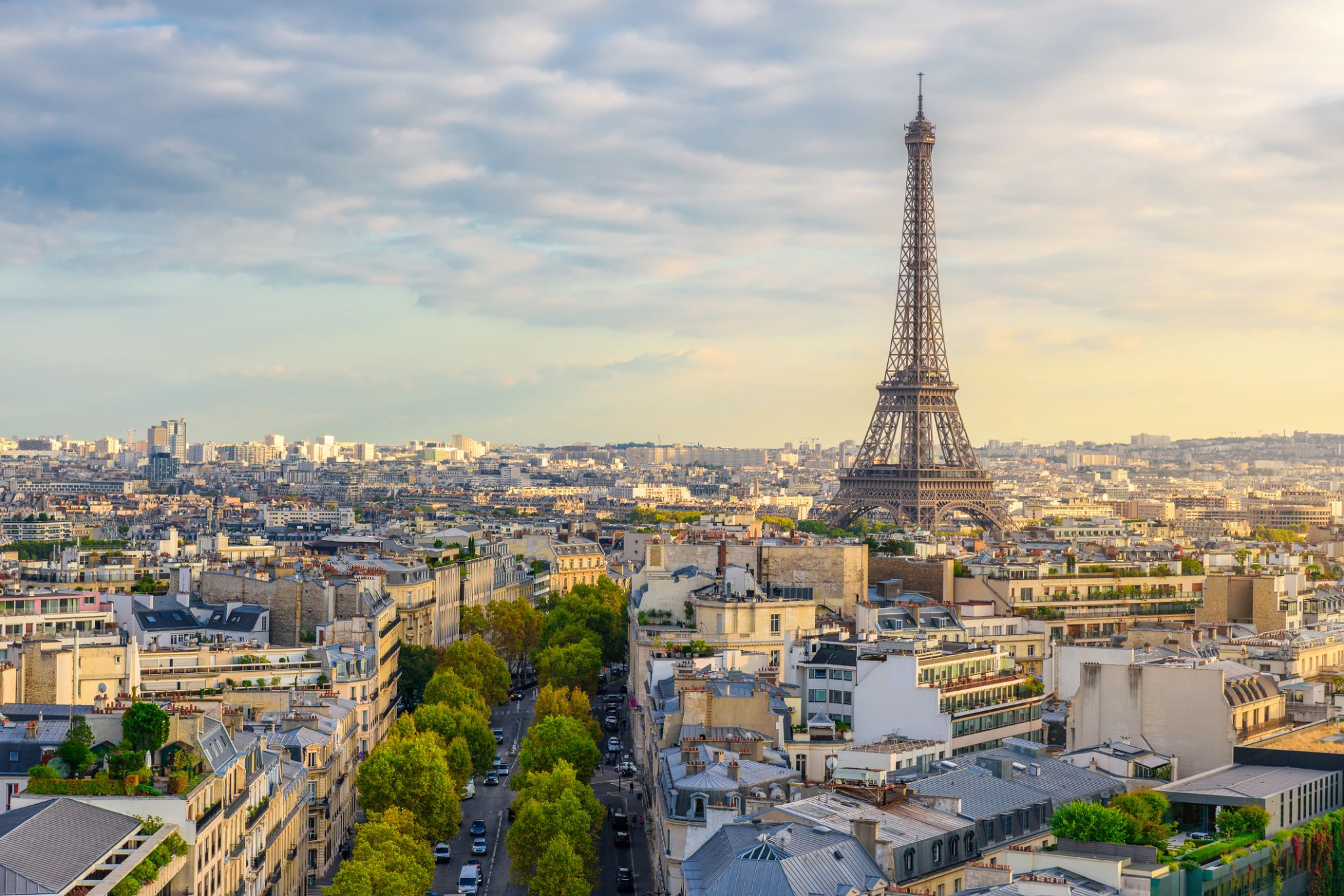 Dzień 40: 08:45-21:00
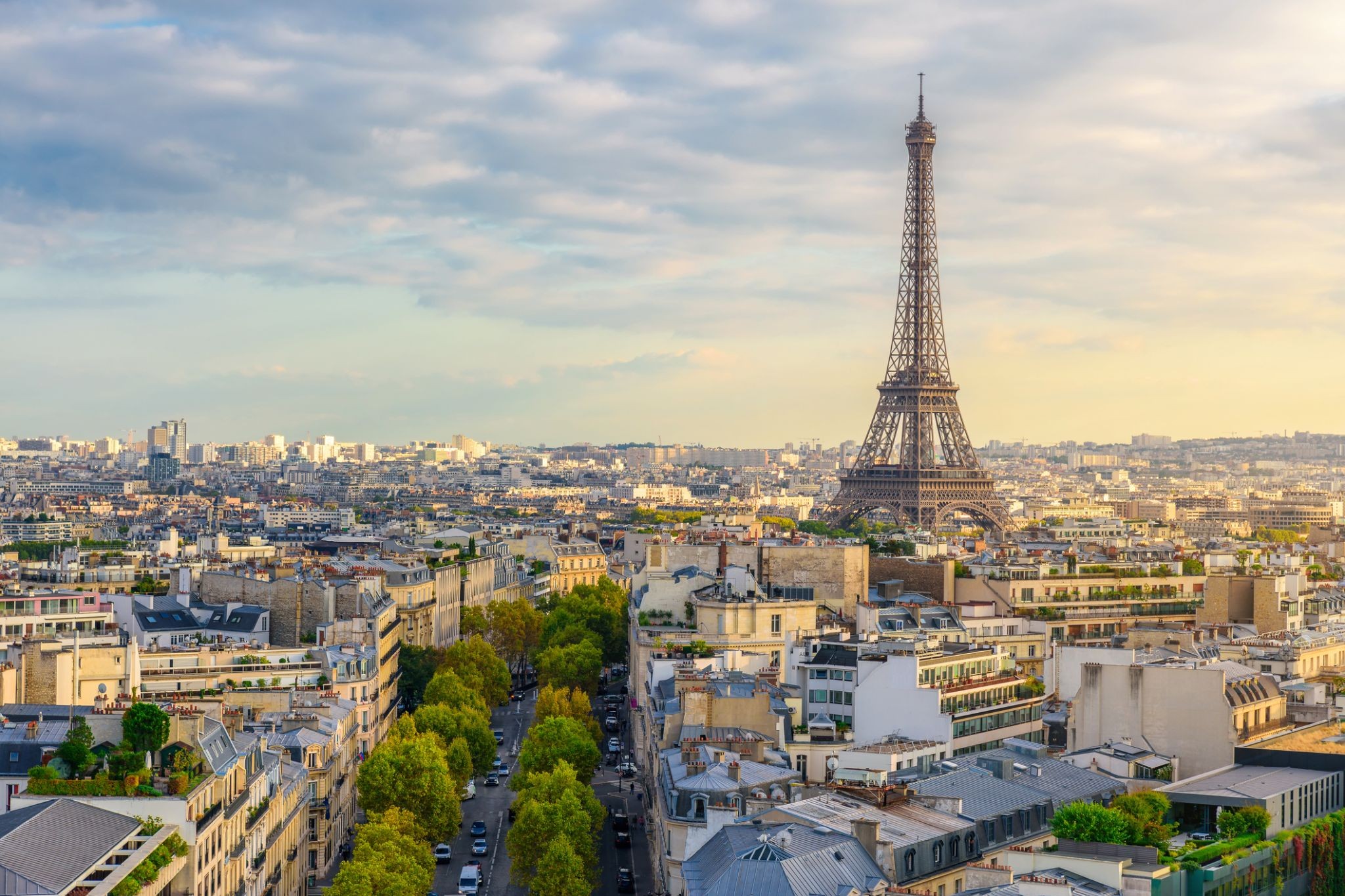
Dzień 40: 08:45-21:00Paryż / Francja
the capital of France, on the Seine River; population 2,203,817 (2006). Paris was held by the Romans, who called it Lutetia, and by the Franks, and was established as the capital in 987 under Hugh Capet. It was organized into three parts—the Île de la Cité (an island in the Seine), the Right Bank, and the Left Bank—during the reign of Philippe-Auguste 1180–1223. The city's neoclassical architecture dates from the modernization of the Napoleonic era, which continued under Napoleon III, when the bridges and boulevards of the modern city were built.
-
 Dzień 41: 11:00-21:00
Dzień 41: 11:00-21:00Dunkirk / Francja
-
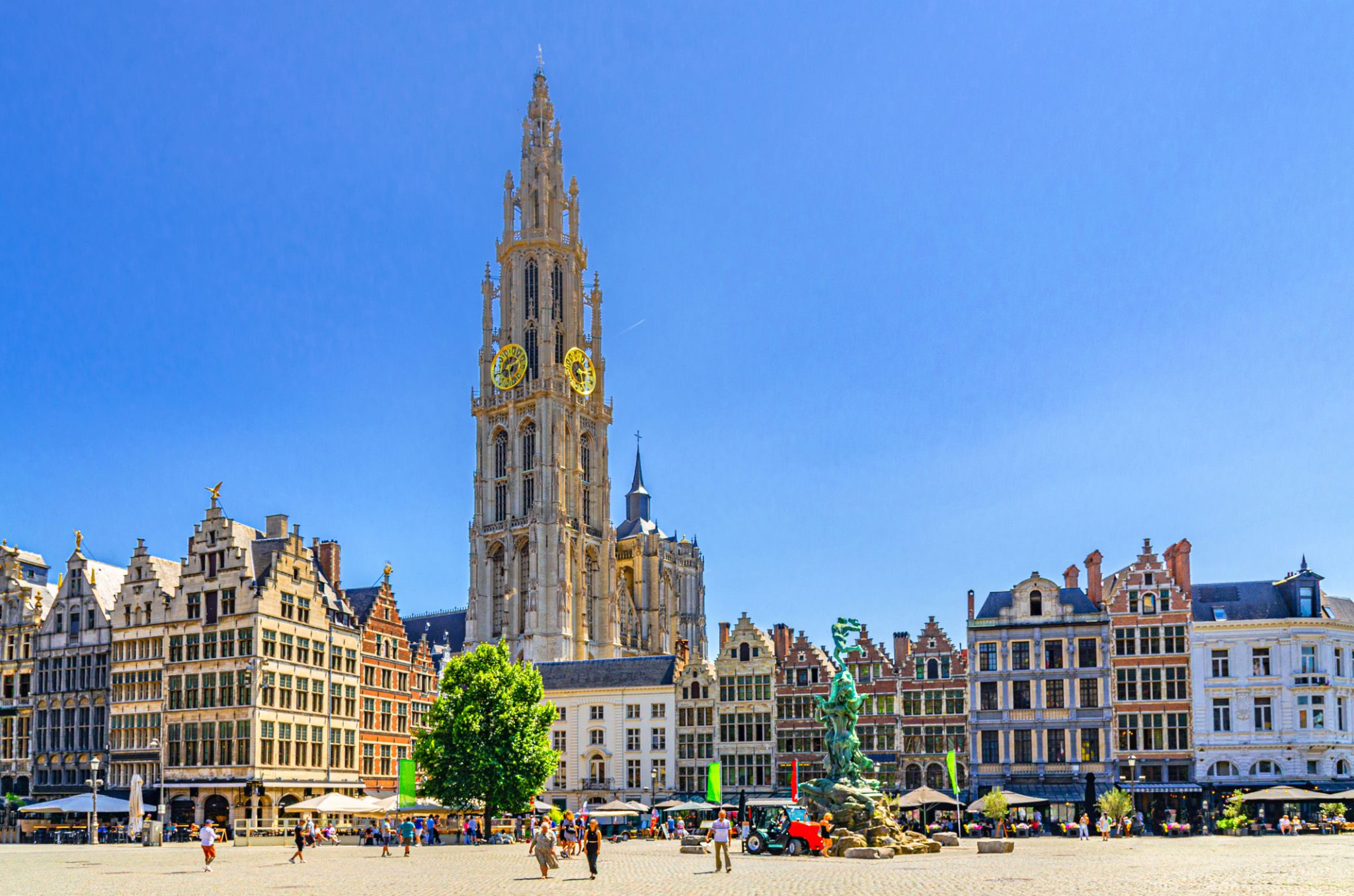 Dzień 42: 09:00
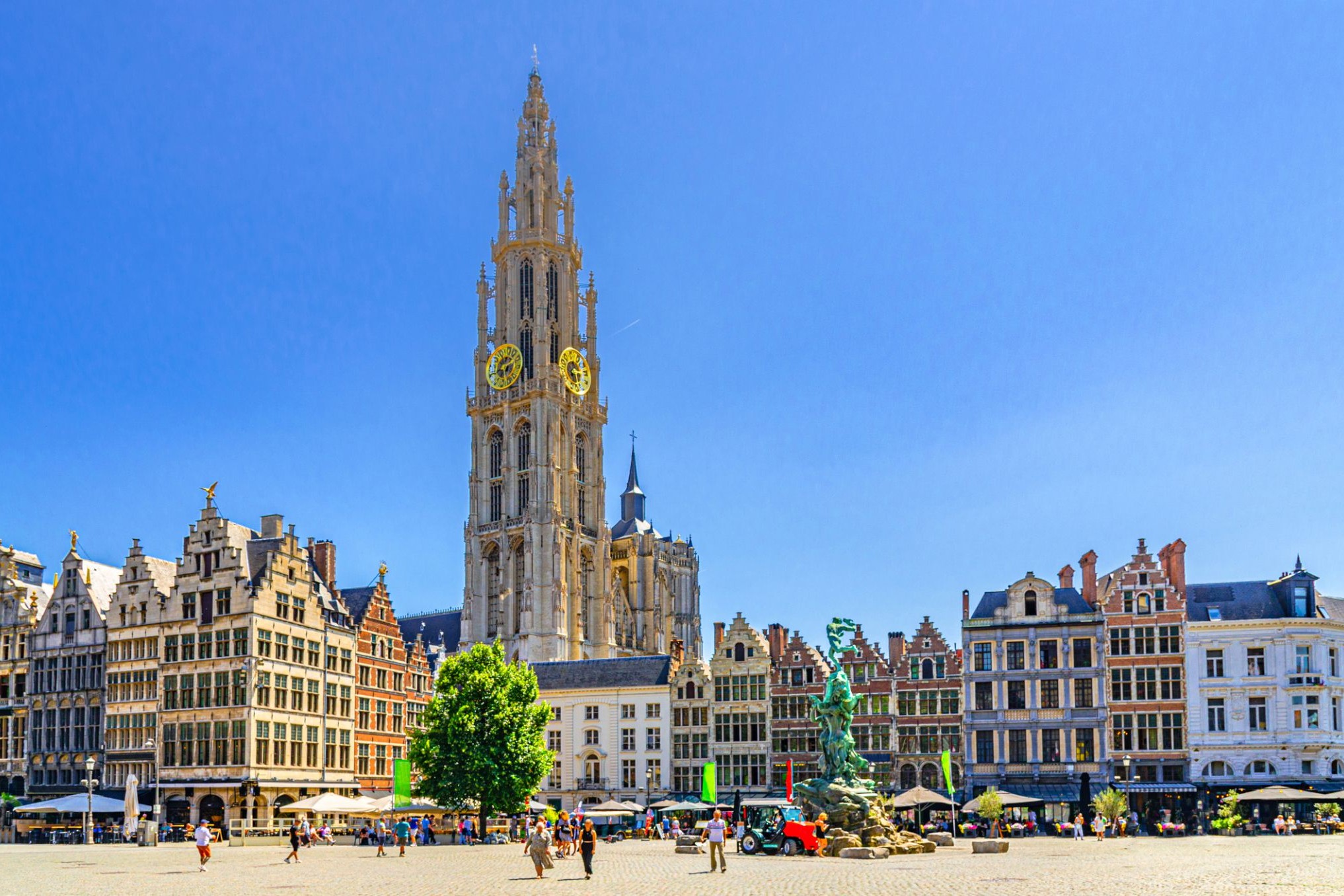
Dzień 42: 09:00Antwerpia / Belgia
a port in northern Belgium, on the Scheldt River; population 472,071 (2008). By the 16th century, it was a leading European commercial and financial center. Flemish name Antwerpen.
-
 Dzień 43: 19:00
Dzień 43: 19:00Antwerpia / Belgia
a port in northern Belgium, on the Scheldt River; population 472,071 (2008). By the 16th century, it was a leading European commercial and financial center. Flemish name Antwerpen.
-
 Dzień 44: 06:00-16:00
Dzień 44: 06:00-16:00Używany
-
 Dzień 45: 07:00-21:00
Dzień 45: 07:00-21:00Paryż / Francja
the capital of France, on the Seine River; population 2,203,817 (2006). Paris was held by the Romans, who called it Lutetia, and by the Franks, and was established as the capital in 987 under Hugh Capet. It was organized into three parts—the Île de la Cité (an island in the Seine), the Right Bank, and the Left Bank—during the reign of Philippe-Auguste 1180–1223. The city's neoclassical architecture dates from the modernization of the Napoleonic era, which continued under Napoleon III, when the bridges and boulevards of the modern city were built.
-
 Dzień 46:
Dzień 46:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
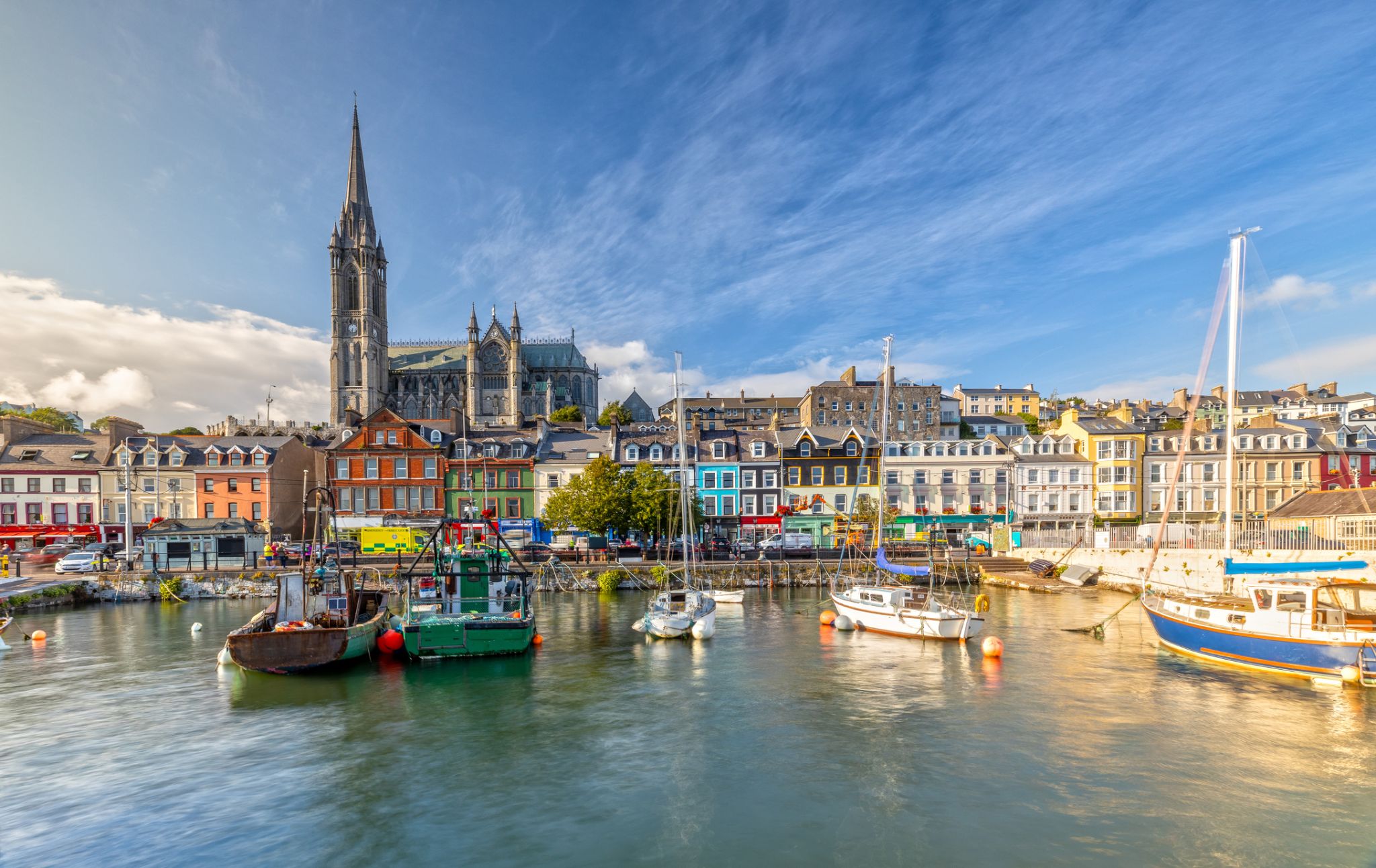 Dzień 47: 07:00-18:00
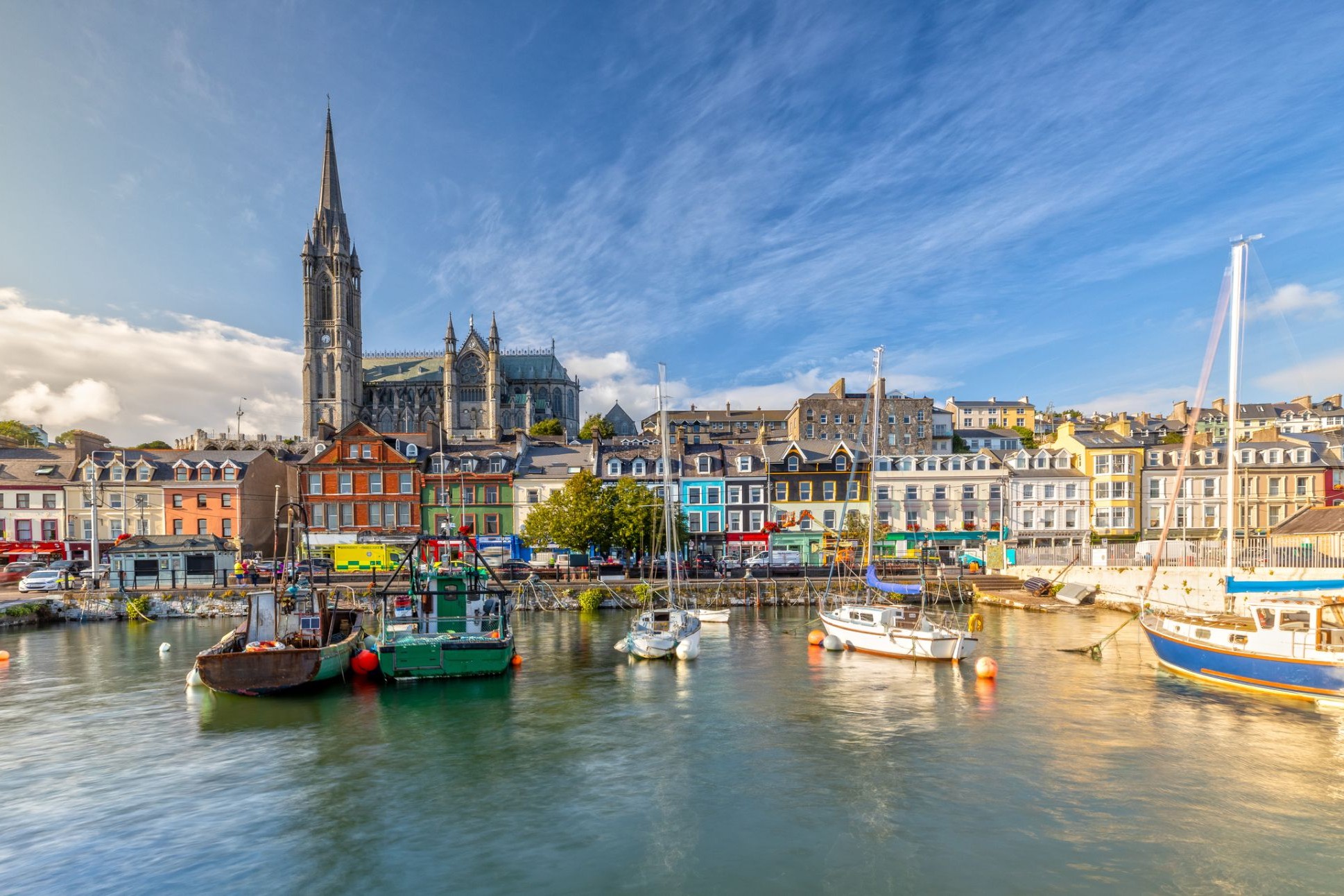
Dzień 47: 07:00-18:00Zatoka (Cork) / Irlandia
Cork is a city in south-west Ireland, in the province of Munster, which had a population of 125,657 in 2016.
The city is on the River Lee which splits into two channels at the western end and divides the city centre into islands. They reconverge at the eastern end where the quays and docks along the river banks lead outwards towards Lough Mahon and Cork Harbour, one of the largest natural harbours in the world.
Expanded by Viking invaders around 915, the city's charter was granted by Prince John, as Lord of Ireland, in 1185. Cork city was once fully walled, and the remnants of the old medieval town centre can be found around South and North Main streets.
The third largest city on the island of Ireland, the city's cognomen of "the rebel city" originates in its support for the Yorkist cause in the Wars of the Roses. Corkonians often refer to the city as "the real capital", a reference to its opposition to the Anglo-Irish Treaty in the Irish Civil War.
-
 Dzień 48: 07:30-17:00
Dzień 48: 07:30-17:00Dublin / Irlandia
Dublin is the capital of, and largest city in, Ireland. It is on the east coast of Ireland, in the province of Leinster, at the mouth of the River Liffey, and is bordered on the south by the Wicklow mountains. It has an urban area population of 1,173,179, while the population of the Dublin Region (formerly County Dublin), as of 2016, was 1,347,359, and the population of the Greater Dublin area was 1,904,806.
There is archaeological debate regarding precisely where Dublin was established by Celtic-speaking people in the 7th century AD. Later expanded as a Viking settlement, the Kingdom of Dublin, the city became Ireland's principal settlement following the Norman invasion. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest city in the British Empire before the Acts of Union in 1800. Following the partition of Ireland in 1922, Dublin became the capital of the Irish Free State, later renamed Ireland.
Dublin is a historical and contemporary centre for education, the arts, administration and industry. As of 2018 the city was listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as a global city, with a ranking of "Alpha -", which places it amongst the top thirty cities in the world.
-
 Dzień 49:
Dzień 49:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
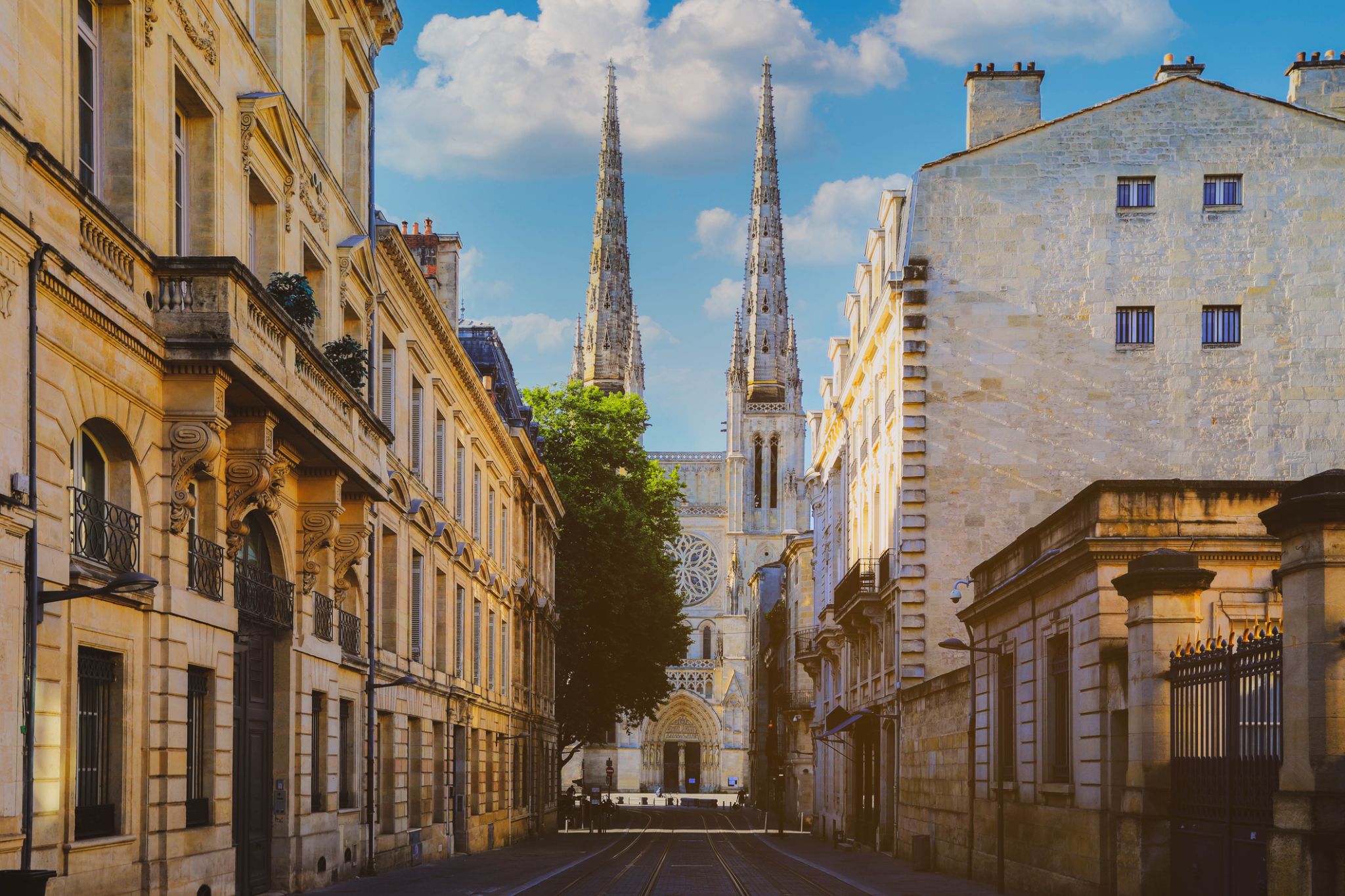 Dzień 50: 12:00
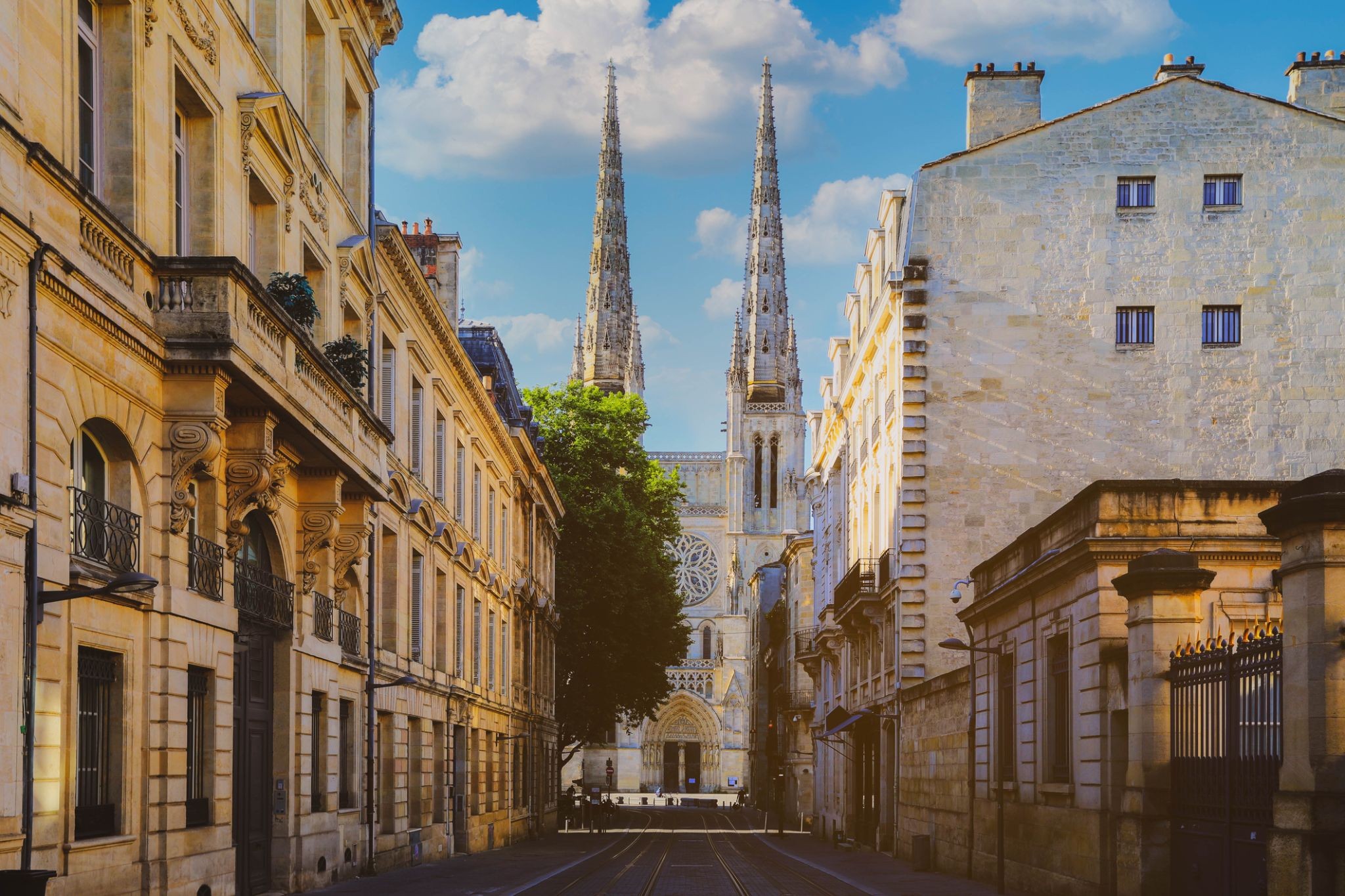
Dzień 50: 12:00Bordeaux / Francja
Bordeaux jest miastem portowym nad Garonną w departamencie Żyronda w południowo-zachodniej Francji.
Sama gmina Bordeaux liczy 246 586 mieszkańców (2014). Wraz z przedmieściami i miastami satelickimi Bordeaux jest centrum metropolii Bordeaux. Z 1 195 335 mieszkańcami w obszarze metropolitalnym jest szóstym co do wielkości we Francji, po Paryżu, Marsylii, Lyonie, Tuluzie i Lille. Jest stolicą regionu Nowa Akwitania, a także prefekturą departamentu Żyronda. Jego mieszkańców nazywa się "Bordelais" (mężczyźni) lub "Bordelaises" (kobiety). Określenie "Bordelais" może również odnosić się do miasta i jego okolic.
Będąc w centrum ważnego regionu uprawy i produkcji wina, Bordeaux pozostaje znaczącym ośrodkiem i wywiera znaczący wpływ na światową branżę winiarską, chociaż w granicach miasta nie odbywa się żadna produkcja wina. Jest siedzibą głównych światowych targów wina, Vinexpo, a gospodarka winiarska w obszarze metropolitalnym przynosi 14,5 miliarda euro rocznie. Wino z Bordeaux jest produkowane w regionie od VIII wieku. Historyczna część miasta znajduje się na Liście Światowego Dziedzictwa UNESCO jako "wyjątkowy zespół miejski i architektoniczny" z XVIII wieku. Po Paryżu Bordeaux ma największą liczbę zachowanych zabytkowych budynków spośród wszystkich miast we Francji.
-
 Dzień 51: 12:15
Dzień 51: 12:15Bordeaux / Francja
Bordeaux jest miastem portowym nad Garonną w departamencie Żyronda w południowo-zachodniej Francji.
Sama gmina Bordeaux liczy 246 586 mieszkańców (2014). Wraz z przedmieściami i miastami satelickimi Bordeaux jest centrum metropolii Bordeaux. Z 1 195 335 mieszkańcami w obszarze metropolitalnym jest szóstym co do wielkości we Francji, po Paryżu, Marsylii, Lyonie, Tuluzie i Lille. Jest stolicą regionu Nowa Akwitania, a także prefekturą departamentu Żyronda. Jego mieszkańców nazywa się "Bordelais" (mężczyźni) lub "Bordelaises" (kobiety). Określenie "Bordelais" może również odnosić się do miasta i jego okolic.
Będąc w centrum ważnego regionu uprawy i produkcji wina, Bordeaux pozostaje znaczącym ośrodkiem i wywiera znaczący wpływ na światową branżę winiarską, chociaż w granicach miasta nie odbywa się żadna produkcja wina. Jest siedzibą głównych światowych targów wina, Vinexpo, a gospodarka winiarska w obszarze metropolitalnym przynosi 14,5 miliarda euro rocznie. Wino z Bordeaux jest produkowane w regionie od VIII wieku. Historyczna część miasta znajduje się na Liście Światowego Dziedzictwa UNESCO jako "wyjątkowy zespół miejski i architektoniczny" z XVIII wieku. Po Paryżu Bordeaux ma największą liczbę zachowanych zabytkowych budynków spośród wszystkich miast we Francji.
-
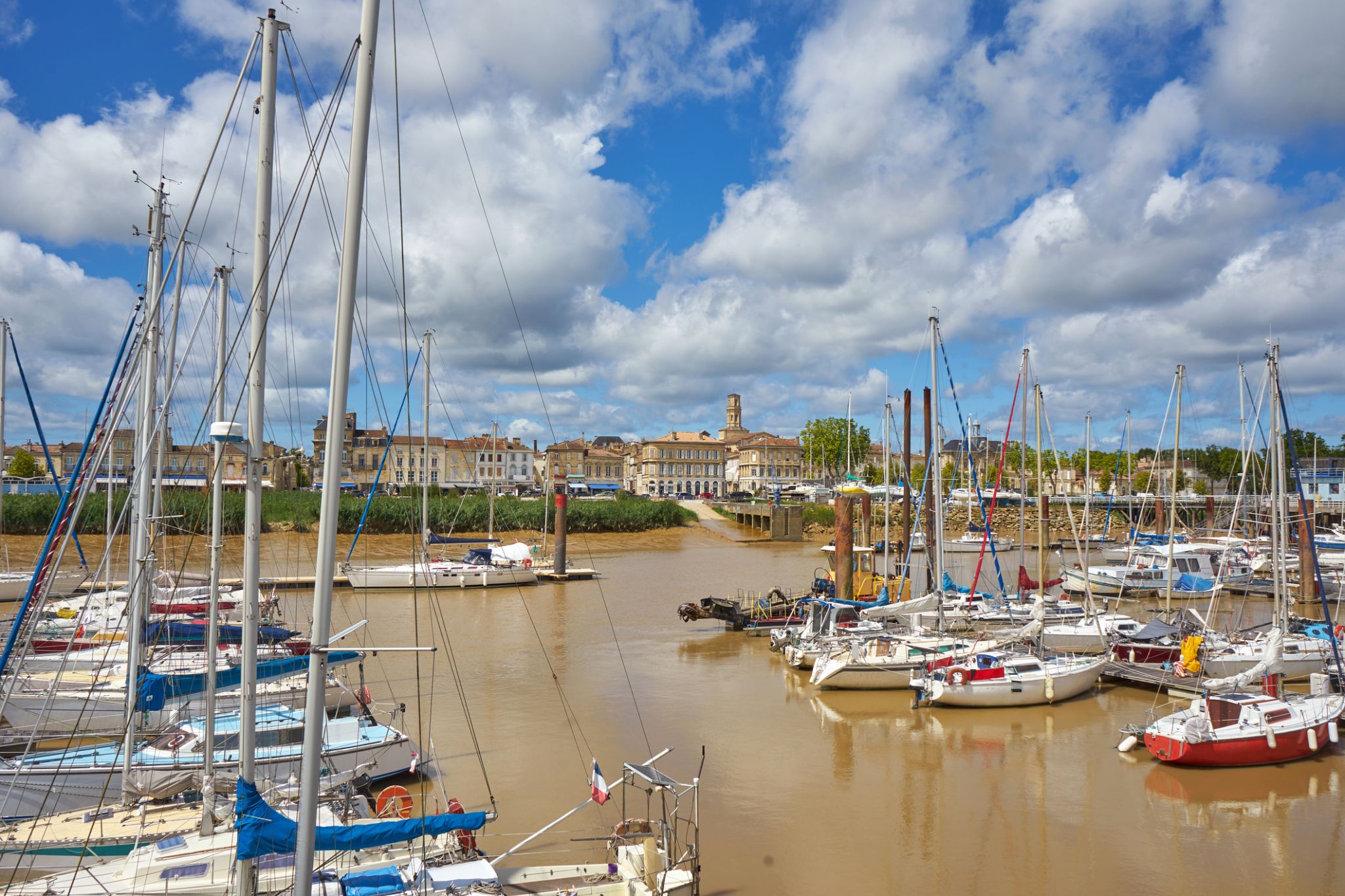 Dzień 51: 15:00-19:00
Dzień 51: 15:00-19:00Pauillac / Francja
-
 Dzień 52: 09:00-19:00
Dzień 52: 09:00-19:00San Sebastian La Gomera San Sebastian la Gomera / Hiszpania
-
 Dzień 53: 08:00-18:00
Dzień 53: 08:00-18:00Gijon / Hiszpania
-
 Dzień 54:
Dzień 54:Dzień na morzu / Morze
-
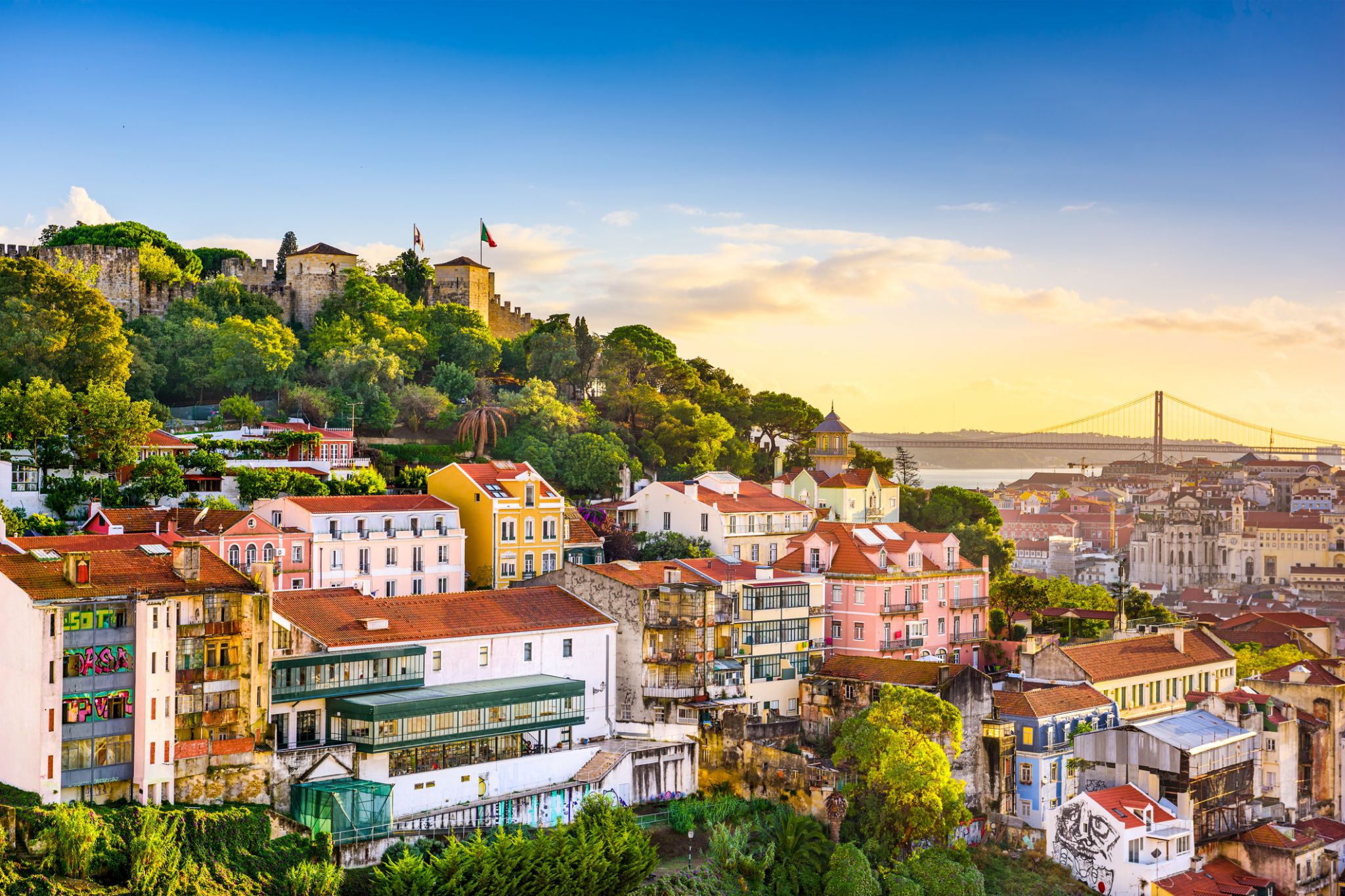 Dzień 55: 06:00-18:00
Dzień 55: 06:00-18:00Lizbona / Portugalia
Lizbona jest stolicą i największym miastem Portugalii, z szacowaną populacją 505 526 mieszkańców w granicach administracyjnych na obszarze 100,05 km². Jej obszar miejski rozciąga się poza granice administracyjne miasta i liczy około 2,8 miliona mieszkańców, co czyni go jedenastym najbardziej zaludnionym obszarem miejskim w Unii Europejskiej. Około 3 milionów ludzi mieszka w aglomeracji lizbońskiej (która stanowi około 27% populacji kraju). Jest to najbardziej wysunięta na zachód stolica kontynentalnej Europy i jedyna położona nad Oceanem Atlantyckim. Lizbona leży na zachodnim Półwyspie Iberyjskim nad Oceanem Atlantyckim i rzeką Tag. Najbardziej wysunięte na zachód obszary jej aglomeracji tworzą najbardziej wysunięty na zachód punkt kontynentalnej Europy, znany jako Cabo da Roca, położony w górach Sintra.





























